
Abstract:
‘In-vitro’ anti-bacterial activity of mother tinctures and potencies of some homoeopathic drugs like Echinacea angustifolia, Belladonna, Calendula officinalis, against plain alcohol was screened against streptococcus, staphylococcus, pneumococcus, citrobacter, acinobacter, e-coli.
Keywords: in-vitro, antibacterial, homoeopathic drugs.
INTRODUCTION:
Since the beginning of this earth, infectious diseases have plagued humanity, evolving with changing life conditions and population expansion. Indigenous cultures in equilibrium with their endemic infectious diseases have been devastated by contact with infections of modern civilisation. Even today, societies in densely populated developing countries where sanitary conditions are very poor are prey of infectious diseases. On the contrary, medical practices too have attracted the panorama of anti-microbial drugs which have radically changed the prevalence and causes of most infectious diseases. However, frequent use of these synthetic anti-microbial drugs leads to development of drug resistant microbes.
In homoeopathy, there are number of drugs which are being clinically used for the treatment of many infectious ailments and some of them are being tested for anti-bacterial activity as well. The present research was undertaken to study the anti-bacterial activity of mother tinctures and potencies prepared from five medicinal plants which are used as medicines for various diseases.
MATERIALS AND METHODS:
‘In-vitro’ screening of anti-bacterial activity of homoeopathic mother tinctures and potencies were carried out against streptococcus, staphylococcus, pneumococus, citrobacter, acinobacter species by agar diffusion method1. Sterile filter paper (Whatman No 1) discs of 6 mm diameter were thoroughly soaked in the respective drugs and subsequently allowed to evaporate its alcohol content. These discs were placed on petri-dishes containing 100 ml of Mueller Hinton agar medium (hi-media chemicals) already inoculated with 24 hours old culture of a selected bacterial strain. Incubation was done at 37˚C for 24 hours. The anti-bacterial activity was observed in terms of inhibitory zone appeared around the filter paper discs and graded as mild to moderate depending upon the area of inhibitory zone.
ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF SOME HOMOEOPATHIC MOTHER TINCTURES AND POTENCIES
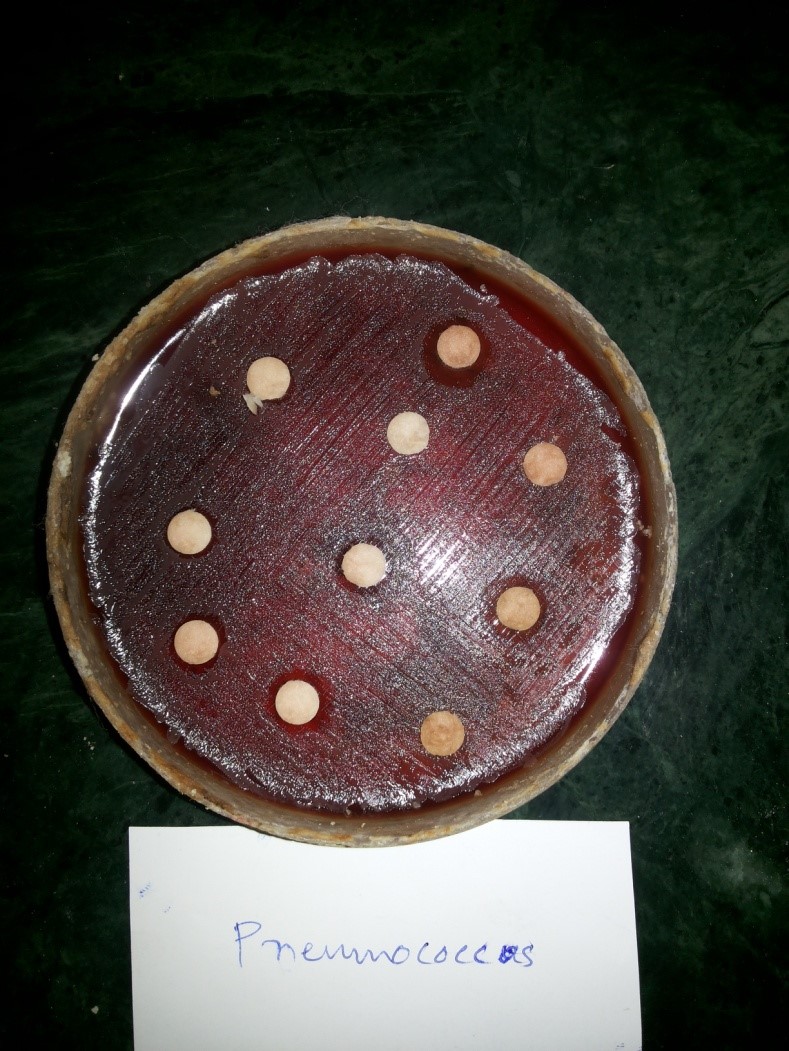
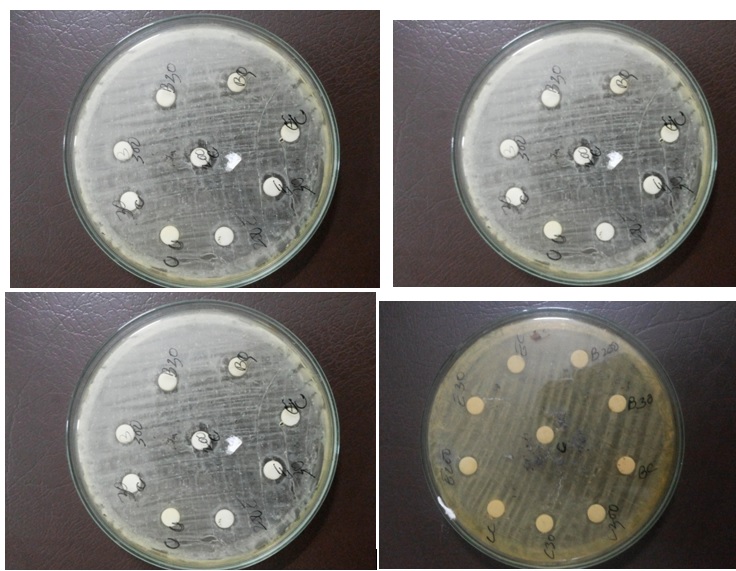
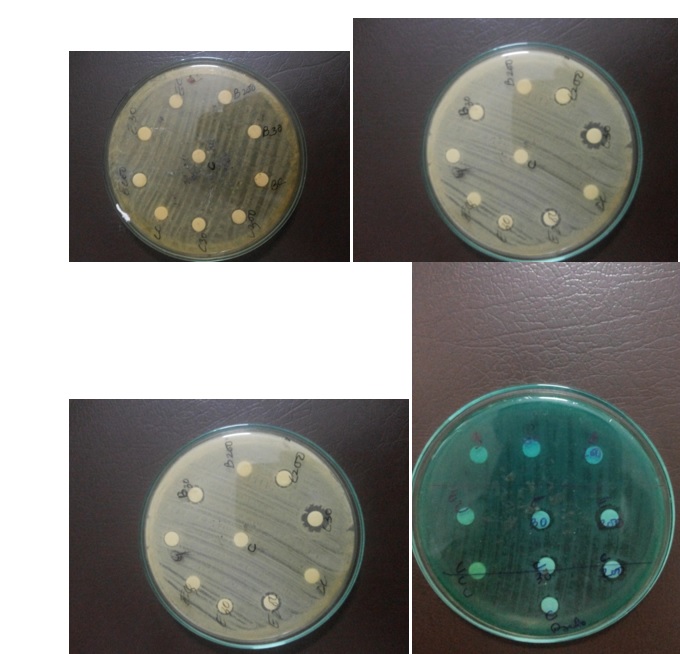

Figure:1-8 Various bacterial strains: 1.Streptococcus 2.Staphylococcus 3.E.coli 4. Acenobacter 5.Citrobacter 6.Pseudomonas 7.Klebsiella 8.Pneumococcus)
Note: Appearance of growth inhibitory zone mild moderate in all the tested organisms treated with homoeopathic mother tincture and potencies.
C- control plain alcohol , BQ,B30,B200 – Belladonna,CQ,C30,c200 –Calendula officinalis– EQ,E30,E200 – Echinacea angustifolia
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION:
Alkaloids, essential oils and several naturally occurring metabolites including organoteterocyclic compounds are reported to possess anti-bacterial, anticancer and other pharmacological activities. Several workers have reported anti-bacterial activity of crude extract of various medicinal plants. In the present study, homoeopathic mother tincture of five medicinal plants were screened for their anti-bacterial activity.10,14,20,25
Echinacea angustifolia, Belladonna, Calendula officinalis are used in alternative system of medicine for treatment of bronchitis, diarrhoea, rheumatism, wounds, tooth-ache and disease of the digestive functions and could be suitable source of natural anti-oxidant activity. Tyagi et18 al have reported anti-bacterial activities in aqueous and alcoholic extracts of leaf. Anti-diarrhoeal and anti-microbial activities in rats were also reported by Lin et al in aqueous and methanolic extracts of leaf of P. guajava. Alpinia galangal wild, is used for the treatment of rheumatic arthritis, inflammation, head-ache, lumbago, bronchitis and diseases of the heart and kidney18. The rhizome produced fall in blood glucose level in normal rabbits. Synthetic alkyl esters similar in structure found in rhizome of A. galangal has been found to possess anti-microbial and bactericidal activities. The volatile oil obtained from Chenopodium ambrosioides Linn, is used as an anthelminthic against intestinal parasites including roundworms, hookworms and intestinal amoebae1. The fresh extract of aerial part has anti-trypanosomal compounds19. Essential oil isolated from Chenopodium ambrosiodes recorded as most powerful licicidal and niticidal activities. Eicchornia cressipessolms, is used as remedy to treat goiter. Valeriana officianalis Linn is an anti-spasmodic and depressant central nervous system and is used in hysteria, hypochondriasis and chorea and allied affections. It also stimulates the immune function of bone marrow cells.
Though synthetic esters have been reported to be anti-microbial and bactericidal. However, in the present investigation, the mother tincture (ie alcoholic extract) of Belladonna, Calendula officinalis, Echinacea angustifolia, mother tincture exhibited mild to moderate anti-bacterial activity against all the strains of microbes tested, while various potencies show moderate to negligible anti-bacterial activity against any of the strains tested.
The anti-bacterial principle observed in mother tincture and various potencies of homoeopathic drugs against all the tested micro-organisms would support to develop an economical, non-toxic and potential anti-bacterial medicine on scientific basis for homoeopathic system of medicine.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT:
We thank the Detya Diagnostic centre, DR KANCHAN BHUTDA, microbiologist for providing the facilities and microbes for the test. We also thank the Central Homoeo Pharmacy, Aurangabad for supplying mother tinctures and potencies of various companies like Lord’s, Bioforce and Schwabe. Also thankful to my teacher and guide Dr V. S. Parashar for providing able guidance during the study. for the first and foremost thanks to DKMM Homoeopathic Medical college and PhD Research centre for providing all necessary infrastructure.
About the author: Dr Mohd Furqan is Dean of DKMM Homoeopathic medical college Prof. & HoD of Organon Guide and PhD researcher of MUHS Nashik. He is member of Review board of Editorial and scientific publication MUHS. He has written various articles in national and international journals and website presented 17 research papers in homoeopathy.
REFERENCES:
- Anantnarayan & Panikar. The Textbook of Microbiology.12th edition 2018.
- The useful plants of India. Publications and Information Directorate, CSIR, New Delhi, (1992):pp 119.
- Akhtar, M.S., Khan, M.A. Malik, M.T., 2002. Hypoglycaemic activity of Alpinia galangal rhizome and its extracts in rabbits, Fitotarapia. 73 (7-8) : 623-628.
- Asolkar, L.V., Kakkar, K.K. and Charke, O.J., 1992. Glossary of Indian Medicinal Plants with active principles. Publications and information Directorate, CSIR., New Delhi,228.
- Bauer, A.W., Kirby, M.D.K., Sherris, J.C. and Turck, M. 1996. Amer. J. Clin.Pathol. 45, 493.
- Boericke, W. 1996., Pocket Manual of Homoeopathic MateriaMedica and Repertory [Rep. Ed]. B. Jain publishers PVT. LTD. New Delhi.
- Chatteerjee, T.C, Ghosh, C.M., Mukherjee, K. and Achary, P.M.R., 1993. Anti-bacterial efficacy of Juniperuscommunis (Linn) leaf extract in-vitro. Ind. J. of Microbiol. 33 (4): 273-275.
- Davey, R.W., McGregor, J.A. and Grange, J.M., 1990a. Screening tests for antibacterial substances in plant extracts. Comp.Med. Res. 4: 1-7.
- Davey, R.W,McGregor, J.A. and Grange, J.M., 1990B. Higher plants as possible sources of new antibiotics active against Staphylococcus aureus. Eur. Clin. Lab. 94 (4): 12-16.
- Davey, R.W., McGregor, J.A., Grange, J.M., 1992. Quality control of Homoeopathic medicines. Br. Hom. J. 81, 78-81 & 82-85.
- Dhingra, V., Pakki, S.R. and Lakshmi Narasu, M., 1999. Anti-microbial activity of artemisinin and its precursors. Curr. Sci.. 78 (6): 709-713.
- Ebringerova, A., Kardosova, A., Hromadkova, Z. and Hribalova, V., 2003. Mitogenic and comitogenic activities of polysaccharides from some European herbaceous plants. Fitoterapia. 74 (1-2): 52-61
- Garg, S.C. and Jain, R.K., 1998. Anti-microbial efficacy of essential oil from Curcuma caesia. Ind. J. Microbiol. 38:169-170.
- Grange, J.M., Davey, R.W. and Jonas, S.K., 1987. A study of the bactericidal and bacteriostatic effects of preparations derived from plant material used in herbal and homoeopathic medicine. Comp. Med. Res. 2: 135-140.
- Hiremath, S.P., Swamy, H.K.S., Shrishailappa, B., Meena, S. and Badami, S., 1996. Anti-bactrial and fungal activities of strigadensiflora and strigaorobinchioides. Ind. J. of Pharm. Sci. 58 (4): 174-176.
- Jimenez-Escrig, A., Rincon, M., Pulido, R. and SauraCalixto, G., 2001. Guava fruit (Psidiumguajava Linn) as a New source of anti-oxidant dietary fiber. J. of Agri& Food Chem. 49 (11): 5489-5493.
- Kirtikar, K.R. and Basu, B.D., 1980a. Indian Medicinal Plants. L.M. Basu Publications Allahabad. 2. 1046-1048
- Kirtikar, K.R. and Basu, B.D, 1980b. Indian Medicinal Plants. L.M. Basu publications. Allahabad. 14, 2445-2447.
- Kirtikar, K.R. and Basu, B.D., 1980c. Indian Medicinal Plants. L.M. Basu Publications, Allahabad. 2. 1310-1311.
- Kiuchi, F., Itano, Y., Uchiyama, N., Honda. G., Tsubouchi, A., Shimada, J.N. and Aoki. T., 2002. Monoterpenehydroperoxides with trypanocidal activity from Chenopodiumambrosiodes, J. of Nat. Products. 65 (4). 509-512.
- Kulkarni C.Y., Bharathi, P. and Patil, C.V., 1992. Anti-microbial activity of Luffatuberosa (Roxb). Ind. J. of Microbiol. 32 (4): 493-495.
About the Author:
Mohd Furqan, V.S Parashar, Bhutda Kanchan





