ABSTRACT:-
The term posology is derived from the greek and posos meaning how much (DOSE) and logos meaning study or discourse. Posology is defined as the doctrine of dosage. By dose, one means the quantity of the medicine to be taken at one time.
Having selected a remedy in accordance with the principles of similia, then comes the most important question of its administration, as to the selection of dose, potency, and the interval at which it may need any repetition.
KEYWORDS: Posology, dose, potency, repetition, susceptibility, constitution
INTRODUCTION:-
DEFINITION OF POSOLOGY:-
Posology means the doctrine of doses of medicine. The terminology of “dose” is derived from the greek word “dosis” which means ‘a giving’ the quantity of a drug or other therapeutic agent to be taken or applied all at a time or in fractional amounts within a stated period of time.1
DEFINITION OF HOMOEOPATHIC POSOLOGY:-
A homoeopathic “dose” means the particular preparation of medicine used, the quantity and form of that preparation as well as the number of administration of the medicine.1
In short, homoeopathic dose include potency, form, quantity and number of administration.1
The study of doctrine of these doses is known as “posology”.1
After selecting a remedy in accordance with the principles of similia, then comes the most important part of its administration, as to the selection of potency, dose and interval at which it may need any repetition.2
But this can only be done if the homoeopathic physician is well acquainted with the fundamental laws of pharmaceutics, i.e. source of homoeopathic drugs and the process in which they are prepared and used in sickness.2
SELECTON OF POTENCY:-1
It is one of the important task after selection of medicine. It has been shown experimentally that in spite of the correctly selected medicine on the basis of totality of symptoms, it will not act curatively unless given in proper potency.
Broad division of potency:-
- Low :-potency below 30
- Medium :- potencies between 30 -1M
- High :- potencies above 1M
Following points will help in selection of potency:
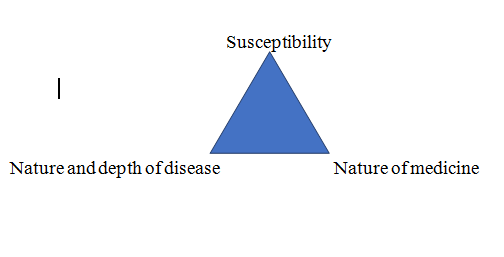
1. SUSCEPTIBILITY: –1
It is the only guide for the selection of potency. MORE THE SUSCEPTIBILITY HIGHER THE POTENCY, LESS THE SUSCEPTIBILITY LOWE THE POTENCY. For this the physician must be qualified through the knowledge of allied subjects and must be unbiased. Following points effects susceptibility: –
a) AGE: –
Child and young require higher potency because of lesser wear and tear of tissues and organs because of high susceptibility.
Old people require medium or lower potency because of more wear and tear of tissues and organs because of low susceptibility.
b) SEX: –
Females and males those are under less stress, worries and anxieties, their nervous system are generally quiet in nature and having moderate degree of susceptibility they require medium potency.
Females and males of irritable, sensitive nature, having high susceptibility require high potency.
c) Habit and environment:-1
| Higher potencies are best adapted to | Lower potencies are best adapted to |
| Persons engaged in high intellectual and mental work.Sedentary occupation.Excitement of the imagination and emotions.Long sleep.An effeminate life. | Person engaged in physical labour without much mental exertion.Druggists, perfumers, chemical workers.Idiots, imbeciles and the deaf and dumb.Who sleep less.Whose food is course |
d) Constitution and temperament:-1
| High potency are best adapted to | Low potency are best adapted to |
| Sensitive person of nervous, sanguine and choleric temperament.Intellectual persons, quick to act and react.Zealous and impulsive. | Torpid and phlegmatic individuals, dull of comprehension and slow to act.Coarse fibred, sluggish individuals of gross habits.Those how possess great muscular power but require a powerful stimulus to excite them |
2. NATURE AND DEPTH OF THE DISEASE:-1
| HIGH POTENCY | LOWER POTENCY |
| Acute disease with no structural change.Acute manifestation of chronic disease at the beginning of organic change or at functional level. Chronic diseases without organic changes.Primary manifestation of psora, syphilis and sycosis.Previously treated with crude homoeopathic or allopathic medicines.Dynamic pathology. | Acute disease with low vitality.Acute manifestation of chronic disease with organic changes.Chronic disease with organic changes.Secondary manifestation of psora, syphilis and sycosis.Difficult and incurable diseases require low potency to avoid the aggravation.Organic pathology. |
3 NATURE OF MEDICINE: –1
- Nosodes : – it should be given in high potency
- Some medicines work best in lower potencies example: – Crataegus oxyacantha Q
- Some medicines are reputed to vary with their potency example:- Hepar sulphuricum.
- Great care should be taken for the selection of potency of deep acting medicines.
SELECTION OF DOSES: –
Dose means the quantity of medicine required to produce a direct effect on the human body both in state of health and disease. In order to produce this effect, fixation of quantity of the drug is required which can be determined by experience or experiments.
As a rule, the dose varies according to the age, temperament, and state of health of individuals.
Master Hahnemann says, ‘the suitableness of a medicine for any given case of disease does not depend on its accurate homoeopathic selection alone, but likewise on the proper size, or rather smallness of the dose.’ According to the Master, the dose should neither be too large nor too strong if it is quite homoeopathic in its selection.
Master Hahnemann says, “A medicine whose selection has been accurately homoeopathic must be all the more salutary the more its dose is reduced to the degree of minuteness appropriate for a gentle remedial effect.”2
Some doses are of various types: –3
- MAXIMUM DOSE: – It is the maximum or largest quantity of medicine, not harmful to human life.
- FATAL DOSE: -It is known as toxicological or narcotic dose. It is such amount of dose, which can cause death of living being. The amount of drug depends on the toxicity of the substance.
- DIVIDED DOSE: – It is fractional dose, after dividing from big dose, which are taken at short interval.
- MINIMUM DOSE: – The quantity of medicine which is though smallest in quantity, produces the least possible excitation of the vital force. It is sufficient to effect the necessary changes in it.
APPROXIMATE DOSE OF HOMOEOPATHIC MEDICINES:-3
| ADULTS | CHILD | INFANT | |
| (above 14 years) | (3 to 14 years) | (Up to 2years) | |
| Powders | 1 grain | ½ grain | ¼ grain |
| Tinctures | 1 drop | ½ drop | ¼ drop |
| Pills | 2 pills | 1 pill | ½ pill |
| Globules | 4 globules | 2 globules | 1 globule |
REPETION OF DOSE: –1
Factor which are responsible for the repetition of dose are: –
Condition and progress of the patient
Nature of disease Nature of remedy
- CONDITION AND PROGRESS OF THE PATIENT: –1
- Perceptible and continued progress of the improvement contraindicates repetition (section 245, 5th edition).
- Repeat the dose only when improvement ceases.
- Repetition may be continued till either recovery ensues or different groups of symptoms arise, and thus, demands a different remedy (Section 248, 5thedition).
- NATURE OF THE DISEASE: –1
- ACUTE DISEASE:-
- As per 5thedition (in centesimal scale) : –
In acute disease repetition may be 24 hourly, 12 hourly, 8 hourly, 4 hourly. In most acute case, every hour, as often as every 5 minute.
- As per 6th edition(in 50 millesimal scale): –
In acute disease, every 2, 3, 4 or 6 hourly repetition can be done in urgent cases repetition can be done every hourly.
- CHRONIC DISEASE : –
- As per 5th edition (in centesimal scale): –
Repetition should be every 14, 12, 10, 8 , 7 days. Lower potency can be repeated frequently in chronic diseases.
- As per 6th edition (in 50 millesimal scale) : –
Large doses and repeated doses were advised by Master Hahnemann.
- NATURE OF REMEDY :-1
- POTENCY :-
- Medicines in lower potency :- frequently repetition
- Medicines in higher potency: -not frequently repeated.
- DURATION OF ACTION:-
- Deep acting remedy:-
Medicines obtained from elements, compounds (inorganic and organic), minerals and nosodes have longer duration pf action hence repeated less frequently.
- Short acting remedy : –
Medicines obtained from vegetable and animal sources have shorter duration of action and can be repeated frequently.
CONCLUSION:-
From the above description, it is clear that not only reaching the most simillimum medicine can cure the case unless until given in proper quantity and quality (potency).
All these three points together reach to the goal of cure, for this one must be clear about all the concepts of homoeopathy, susceptibility, nature of diseases (pathology and practice of medicine), nature of medicine (source). With this knowledge, one can easily reach towards the mission of physician as stated by Master Hahnemann in Aphorism no. 1.
REFERENCES:-
- Partha MP, Mandal B. A Text Book of Homoeopathic Pharmacy. B. Jain Publishers; 2001.
- Rawat PS. Select Your Doses & Potency. B. Jain Publishers; 2002 Jun 30.
- Banerjee NK, Sinha N, Saha HP. A treatise on Homoeopathic Pharmacy. New Allen; 1980.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR: –
NAME: – DR JASPREET KAUR KAPOOR
MD (PGR), DEPARTMENT OF HOMOEOPATHIC MATERIA MEDICA,
SRI GURU NANAK DEV HOMOEOPATHIC MEDICAL COLLEGE, LUDHIANA.