
Abstract:
In homeopathy, HIV infection is approached with a holistic perspective, focusing on individualized treatment based on a patient’s unique physical and mental characteristics. While not a substitute for conventional antiretroviral therapy, homeopathic remedies aim to alleviate symptoms, improve the patient’s quality of life, and potentially delay disease progression. Studies suggest that homeopathic treatment can positively impact HIV progression in some cases, particularly in those with more advanced symptoms, although more research is needed.
Epidemiology:
The epidemiology of HIV, or the study of its distribution and determinants, reveals a global pandemic that began in the early 1980s. HIV is primarily transmitted through specific routes including sexual contact, sharing contaminated needles, mother-to-child transmission, and exposure to infected blood. While progress has been made in reducing new infections, HIV remains a major global public health concern, with an estimated 40.8 million people living with HIV at the end of 2024.
Key Word:
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus), AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome), antiretroviral therapy (ART), and opportunistic infections.
Introduction:
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the body’s immune system, specifically the CD4+ T cells, leading to a weakened immune response. This can progress to Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS), the most advanced stage of HIV infection, where the immune system is severely compromised, making the individual susceptible to opportunistic infections and certain cancers. HIV is transmitted through specific bodily fluids, including blood, semen, vaginal fluids, and breast milk. While there is no cure for HIV, effective antiretroviral therapy (ART) can significantly slow down the virus’s replication, allowing individuals to live long, healthy lives and reducing the risk of transmission.
There are two types of HIV virus:
- HIV-1: It is the most common type of HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus). The virus attacks your body’s immune system by destroying CD4 cells, which help your body fight infections. This can lead to AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome).
- HIV-2: It is a type of human immunodeficiency virus, distinct from HIV-1, though both cause similar symptoms and can lead to AIDS. HIV-2 is primarily found in West Africa and is characterized by lower viral load, slower progression to AIDS, and potentially lower pathogenicity compared to HIV-1. While less prevalent globally, HIV-2 has spread due to migration and globalization.
Pathophysiology:
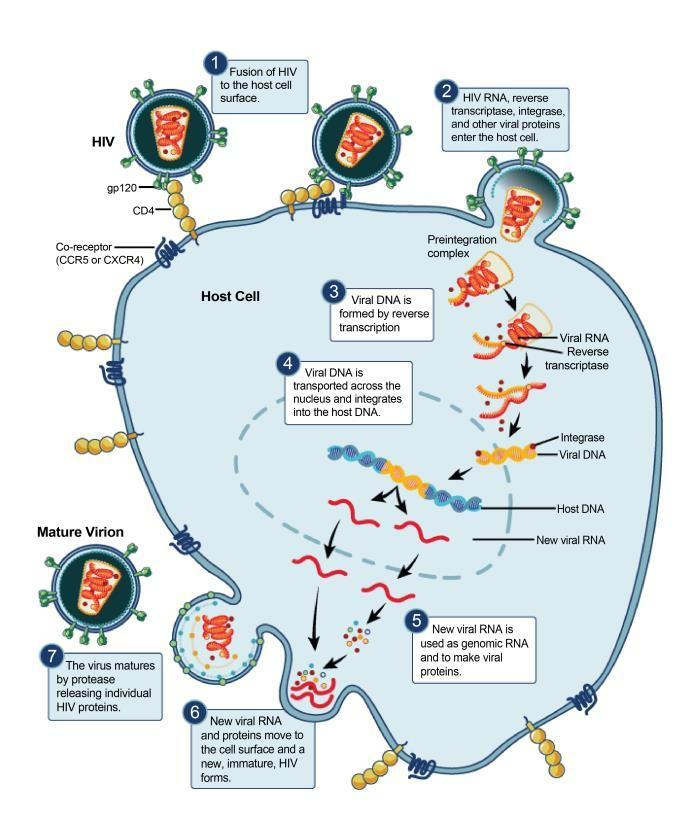
HIV involves the virus infecting and destroying CD4+ T cells, leading to a weakened immune system and ultimately, AIDS. HIV’s ability to integrate its genetic material into the host’s DNA results in a lifelong infection. This process also includes viral replication, mutation, and the potential for the virus to become resistant to treatment.
Clinical Approach:
The clinical approach to HIV involves prompt antiretroviral therapy (ART) to manage the infection and prevent its progression to AIDS. ART, a combination of HIV medicines, is crucial for reducing viral load and protecting the immune system, enabling individuals with HIV to live long, healthy lives and reducing the risk of transmission.
Sign And Symptoms:
Early Stage Symptoms (Acute HIV Infection):
- Flu-like symptoms: Fever, fatigue, headache, muscle aches, sore throat, swollen lymph nodes, and rash.
- Mouth sores: Including thrush (yeast infection).
- Diarrhea: Can be mild or severe.
- Weight loss: Can be noticeable in some individuals.
- Night sweats: Excessive sweating during sleep.
Chronic HIV Infection:
- Swollen lymph nodes: Can persist or worsen.
- Weight loss: May continue or become more pronounced.
- Night sweats: May continue or become more severe.
- Oral thrush: Yeast infection in the mouth and throat.
- Pneumonia: Increased susceptibility to lung infections.
- Gum infection: Can be a sign of weakened immunity.
AIDS (Stage 3):
- Rapid weight loss: Significant and unexplained weight loss.
- Prolonged diarrhea: Can be severe and debilitating.
- Extreme tiredness: Profound fatigue that doesn’t improve with rest.
- Swollen lymph nodes: Can be a persistent symptom.
- Night sweats or fever: May be severe and persistent.
- Opportunistic infections: Infections that take advantage of a weakened immune system, such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, and certain cancers.
- Neurological disorders: Can include memory loss, depression, and other cognitive issues.
- Skin problems: Such as lesions, rashes, or unusual growths.
Investigation:
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) infection is investigated through a series of tests that detect antibodies, antigens, or the virus itself.
Types of HIV Tests:
- Antibody Tests:
These tests look for antibodies produced by the body in response to HIV infection. They are commonly used in rapid tests and at-home kits.
- Antigen/Antibody Tests:
These tests detect both HIV antibodies and antigens (proteins of the virus) in the blood.
- Nucleic Acid Tests (NATs):
These tests directly detect the virus (HIV RNA) in the blood, also known as viral load testing.
Management:
The primary management strategy for HIV/AIDS is antiretroviral therapy (ART), which involves taking a combination of HIV medicines daily or on a schedule to control the virus. While ART doesn’t cure HIV, it effectively suppresses the virus, allowing people with HIV to live long and healthy lives and reducing the risk of transmission.
Homoeopathic Management:
HIV is a chronic viral disease that weakens the immune system by destroying CD4 cells. While antiretroviral therapy (ART) controls viral load, Homoeopathy plays a complementary role by strengthening the vital force, enhancing immunity, reducing opportunistic infections, and improving quality of life. Treatment is based on individualization and miasmatic background (mainly sycotic-syphilitic).
Commonly indicated remedies include:
Arsenicum album, Phosphorus, Sulphur, Kali carb, Tuberculinum, Carcinosin, Bryonia alba, Calcarea carbonica, Nux vomica,and Syphilinum, selected according to the totality of symptoms. Supportive remedies like Echinacea and tissue salts may also be used.
Homoeopathy does not cure HIV, but it helps in boosting immunity, reducing opportunistic infections, and improving overall well-being when used alongside ART.
- Arsenicum album – Great weakness, anxiety, restlessness, burning pains, recurrent infections.
- Phosphorus – Repeated chest infections, bleeding tendency, anxiety, craving for cold drinks.
- Sulphur – Skin eruptions, night sweats, heat, itching, weakness.
- Kali carbonicum – Weakness, breathlessness, night sweats, stitching pains.
- Tuberculinum – Rapid emaciation, recurrent chest complaints, poor vitality.
- Mercurius solubilis – Ulcerations, foul discharges, glandular swellings, excessive salivation.
- Carcinosin – Weak immunity, genetic predisposition, recurrent infections, emotional sensitivity.
- Syphilinum – Ulcerations, destructive tendencies, relapsing fevers.
- Bryonia alba- febrile states, respiratory affections, joint/muscle pains, and weakness with irritability.
- Calcarea carbonica – weakened immunity, recurrent infections, glandular swellings, chronic fatigue, and failure to thrive.
- Nux vomica – Digestive disturbances, drug side-effects (antiretroviral intolerance), nervous irritability, and loss of sleep.
Reference:
- Organon Of Medicine By Dr.Samuel Hahnemann
- Hiv/Aids And Homoeopathic Management By Ccr Homoeopathy
- Boericke’s Homoeopathic Materia Medica With Repertory By William Boericke
- Allen’s Keynotes By H.C.Allen
- Synoptic Key Of The Materia Medica By Dr.C.M.Boger Lectures On Homoeopathic Materia Medica By Dr.James Tyler Kent





