About author
Dr Veena Karanth
PG Scholar, Department of Practice of Medicine
Government Homoeopathic Medical College & Hospital
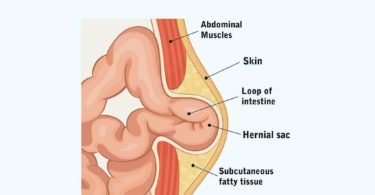
Urolithiasis is derived from the Greek words “ouron” which means “urine” and lithos which means “stone”. Urolithiasis refers to the accretion of hard, solid and non-metallic minerals in the urinary tract
Urolithiasis refers to the accretion of hard, solid and non-metallic minerals in the urinary tract.
Urinary stones are the third most common affliction of the urinary tract.Urolithiasis affects 5-15% of the population worldwide. Recurrence rates are close to 50% and the cost of treatment for urolithiasis to individuals and society is high.Calcium oxalate or phosphate stones are most common about 70% of all urinary stones seen in economically developed countries. Kidney stone is quite common and usually affects people who are between 30 and 60 years of age.
It is estimated that renal colic (severe pain caused by a kidney stone) affects about 10-20% of men, and 3-5% of women. In India, 12% of the population is expected to have urinary stones, out of which 50% may end up with kidney damage.
Urolithiasis can damage kidney tissue if untreated and can be very painful. In other system of medicine there usually management is surgical intervention but with increased recurrence.
Homeopathy is known to treat Urolithiasis by its holistic approach with which it can relive the pain, dissolve the stone and prevent urinary calculi.
HOMEOPATHIC THERAPEUTICS:
CALCAREA CARBONICA: According to Boericke in persons of scrofulous type, who take cold easily, leuco-phlegmatic temperament they are fat, fair, flabby and perspiring and cold sour.Urine is dark, brown, sour, fetid and abundant, with white sediment, bloody.
Clark says – There is tenesmus of the bladder and burning pain in the urethra with too frequent emission of urine at night. Urine is a brownish red, acrid, pungent, and fetid smell, with white and mealy sediment.
CAUSTICUM: According to Boericke in dark-complexioned and rigid-fibered persons, involuntary urination when coughing, sneezing. Expelled very slowly, and sometimes retained. Involuntary urination at first sleep of night; also from slightest excitement. Retention of urine after surgical operations. With loss of sensibility on passing urine .
According to Clark in contractive pains in the abdomen. Pains in the abdomen in the morning, deep-brown, acrid and corrosive urine. Frequent inclination to urinate with scanty emission.
LYCOPODIUM: According to Boericke in persons who are intellectually keen, but of weak, muscular power. Deep-seated, progressive, chronic diseases. In kidney affections, with red sand in urine. They are Intolerant of cold drinks .craves everything warm. Shooting type of pain across lower abdomen from right to left. Pain in back before urinating, ceases after flow; must strain. Retention of urine. Polyuria during the night. Heavy red sediment
According to Clark in persons having disposition to develop calculi,in cystitis,.hæmaturia from gravel or from chronic catarrh . Renal colic, with stinging, tearing, digging pain in right ureter to bladder, as if some small calculus was tearing its way to bladder. Aching in back before micturition. .Child cries before micturition red sand is found on diaper.
NATRUM MURIATICUM: According to Boericke in ill effects of grief, fright, anger cutting pain in abdomen ,pain after urination .Involuntary urination while walking coughing. Has to wait a long time to pass urine if others are present.
According to Clark in stitching pain in bladder during and after micturition and spasmodic contraction pain in abdomen. Urine, is clear with red sediment, resembling brick-dust With smarting, burning in urethra
NUX VOMICA: According to Boericke, there is irritable bladder; from spasmoidic sphincter. haematuria, ineffectual urging, strangury, renal colic extending to genitals, with dribbling urine.
According to Clarke, strangury, with pressure on urinary organs, troublesome pains in neck of bladder, and painful emission of urine, drop by drop. Spasmoidic contraction of urethra. Urine is turbid, reddish with sediment. Urine sometimes scanty and sometimes copious, haematuria, renal colic, constriction and itching in urethra.
SEPIA OFFICINALIS: According to Boericke, in red, adhesive,sand in urine. Involuntary urination, during first sleep.Chronic cystitis, slow micturition with bearing- down sensation above pubis.
According to Clark in frequent desire to urinate from pressure on bladder. Involuntary discharge of urine at night, especially in first sleep.Cramp in bladder deep-coloured urine, red like blood,turbid ,with red, sandy, very offensive ,cannot be endured in room.
STAPHYSAGRIA: According to Boericke in nervous affections with marked irritability, diseases of the genito-urinary tract, Colic after anger .Cystitis in lying-in patients. Ineffectual urging to urinate in newly married women .Sensation as if a drop of urine were rolling continuously along the channel Burning in urethra during micturition.;when not urinating
According to Clark in Colic with urging to urinate ,spasmodic cuttings, needle-like stitches in region of kidneys .Frequent urination of red urine. Pressure on bladder on waking from sleep.
SULPHUR: According to Boericke in dirty, filthy people, prone to skin affections ,very sensitive to pressure in abdomen ,internal feeling of rawness and soreness. Colic after drinking. Frequent micturition, especially at night .Burning in urethra during micturition, lasts long after. Mucus and pus in urine; parts sore over which it passes. Must hurry, sudden call to urinate.
According to Clark in violent pain in region of kidneys after stooping for long time. Spasmodic pains in loins and inguinal. Aching in small of back all day, especially while urinating smarting and burning in urethra ,redness and inflammation of orifice of urethra .Urine like yeast; muddy, turbid, scanty Small and intermittent stream of urine.
PHOSPHORUS ;According to Boericke, in tall, slender persons, narrow chested, with thin, transparent skin, weakened by loss of animal fluids, with great nervous debility, emaciation, amative tendencies, seem to be under the special influence of Phosphorus Sharp, cutting pains hematuria Turbid, brown, with red sediment Worse by touch; ,physical or mental exertion, lying on left or painful side . Better in dark, lying on right side, cold food.According to Clarke in increased secretion of watery urine with frequent emission of scanty stream of urine. Urine with white, serous, sandy, red or yellow sediment
SARSAPARILLA: According to Boerick and clark it is indicated in nephritic calculi where the patient has gravel, and there is considerable deposit in the urine which looks like grey sand; also pus in urine. Urine is discharged with gravel or small pebbles. Burning sensation in urethra during every urination, Cramps in the bladder, stones in the bladder .Great pain at end of micturition, just as the urine cease to flow.
List of References:
1. Sofia NH, Walter TM. Prevalence and risk factors of kidney stone. GJ FR. 2016; 5(3).(cited on 13/2/18)Available from file:///C:/Users/rashmi/U/PREVALENCEANDRISKFACTORSOFKIDNEYSTONE-article%20(1).pdf
2)Boericke W. Pocket Manual of Homoeopathic Materia Medica & Repertory: Comprising of the Characteristic and Guiding Symptoms of All Remedies (clinical and Pahtogenetic [sic]) Including Indian Drugs. B. Jain publishers; 2002.P144-146,181-182,409-411,459-461,475-477,586-587,607-608,620-621,507-509
3)Clarke J H. A dictionary of practical Materia medica, vol 1,2,3. Delhi. B Jain publishers, 1985,1947, 1978;