Abstract
Surgical science remains essential for addressing advanced structural pathologies, traumatic injuries, and life-threatening conditions requiring mechanical intervention. Homoeopathy, within its philosophical and clinical scope, complements surgical procedures by improving preoperative stability, reducing anxiety, enhancing tissue healing, minimizing post-operative pain, and reducing complications such as infection, suppuration, and delayed recovery. This review presents a comprehensive evaluation of Homoeopathy’s utility in surgical cases, the relevant Materia medica, operative considerations, clinical evidence, and future integrative possibilities. The aim is not to replace surgery but to highlight the therapeutic synergy that arises when dynamic medicinal support accompanies mechanical interventions.
Keyword
Surgical Science, Advanced structural pathologies, Homoeopathy, Post- operative, Materia medica, Therapeutic synergy, Dynamic.
Introduction
Surgery, as described across medical history, restores anatomical integrity through mechanical methods when diseases progress beyond the possibilities of internal medicinal regulation. Hahnemann emphasized that while many diseases require dynamic medicinal treatment, mechanical injuries, wounds, and structural disorganization require surgical aid— with Homoeopathic support to prevent complications and enhance healing .
Homoeopathy’s individualized therapeutic approach provides value across peri-operative phases: regulating haemorrhage, reducing inflammation, correcting susceptibility, improving wound healing, preventing suppuration, managing pain, and supporting emotional stress. Its utility is well-recognized in trauma care, dental surgeries, orthopaedics, gynaecology, ophthalmology, ENT, and wound management. This article consolidates these applications with Materia medica insights and documented evidence.
Homoeopathy has long held a complementary yet significant position in the realm of surgery, offering therapeutic support across pre-operative, intra-operative, and post-operative phases. While surgery addresses structural pathology through mechanical intervention, Homoeopathy enhances surgical outcomes by reinforcing the body’s intrinsic healing capacity.
Remedies such as Arnica Montana for trauma and haemorrhage, Staphysagria for clean incisions, Hypericum for nerve-rich injuries, and Calendula for wound granulation have demonstrated consistent clinical utility. In peri-operative care, Homoeopathy contributes to reducing anxiety, minimizing operative shock, improving pain tolerance, limiting post surgical inflammation, and accelerating tissue repair. In chronic surgical conditions—such as fistula, hemorrhoids, recurrent abscesses, and benign tumors—constitutional prescribing may help reduce recurrence by addressing underlying susceptibility and miasmatic influences. Evidence from clinical trials and observational studies further supports the role of Homoeopathy in enhancing vitality, preventing suppuration, controlling postoperative edema, and improving quality of recovery. Importantly, Homoeopathy does not replace surgical intervention where required; rather, it acts as a synergistic modality that broadens the therapeutic spectrum, reduces complications, and promotes holistic healing. Thus, Homoeopathy remains a valuable adjunct in modern surgical practice, aligning gentle therapeutics with precision-based operative care to achieve optimal patient outcomes.
Aims and Objectives
1. To analyse the scope of Homoeopathy in surgical cases.
2. To examine peri-operative applicability of Homoeopathic therapeutics. 3. To document Materia medica remedies pertinent to surgical conditions. 4. To present existing evidence and explore future integrative perspectives.
Historical Background
Homoeopathic surgeons such as Helmuth, Ludlam, and Younkers contributed significantly to early surgical therapeutics using internal remedies. Their work described successful management of abscesses, fistulae, traumatic injuries, eye inflammations, and wound infections long before antibiotics existed.
The Organon of Medicine provides clear guidance that injuries by external force require surgical manipulation, while internal derangements triggered by such injuries require dynamic medicines. This balance forms the philosophical basis of integrating Homoeopathy with surgical care.
Views of Homoeopathic Stalwarts on Surgery and Its Relation to Homoeopathy
The relationship between Homoeopathy and surgery has been shaped by the insights of several classical stalwarts, each contributing a distinct philosophical and clinical perspective. Dr. Samuel Hahnemann, the founder of Homoeopathy, acknowledged surgery as an indispensable branch of healing. In the Organon of Medicine, he clearly stated that mechanical obstructions, structural deformities, and conditions requiring manual intervention must be managed surgically, while Homoeopathy serves as the curative modality for dynamic diseases. Hahnemann emphasized cooperation rather than conflict between the two disciplines.
James Tyler Kent expanded Hahnemann’s view, stressing that Homoeopathy treats the man in disease, whereas surgery treats the results of disease. Kent criticized excessive surgical interventions but strongly supported surgery when essential—such as for fractures, foreign bodies, and irreversible pathology. He asserted that the constitutional remedy prevents complications and reduces the need for repeated operations.
Richard Hughes, known for his physiological approach, advocated a rational integration of surgery and Homoeopathy. He believed that surgical conditions like inflammation, trauma, and septic states could be improved with indicated remedies, thereby enhancing surgical outcomes.
Dr. C.M. Boger emphasized that Homoeopathic therapeutics can limit the spread of disease, hasten repair, and reduce suppuration. His repertory and synoptic key highlight numerous remedies beneficial in peri-operative and traumatic conditions.
E.A. Farrington and Margaret Tyler focused on remedy pictures useful in trauma, incision healing, and postoperative management. They documented clinical experiences where Homoeopathy minimized pain, promoted granulation, and prevented complications. J.H.
Clarke wrote extensively on surgical cases improving with Homoeopathy—especially abscesses, fistulae, glandular swellings, and traumatic injuries—while clarifying the boundaries of non-surgical management.
R.E. Dudgeon and Ludlam contributed significantly to surgical therapeutics in Homoeopathy. Ludlam’s Surgical Therapeutics remains a classical text demonstrating how remedies can complement operative procedures, reduce shock, and improve recovery. Collectively, the stalwarts agreed that surgery and Homoeopathy are not antagonistic but complementary sciences. Surgery corrects mechanical defects, while Homoeopathy enhances the vital force, reduces postoperative morbidity, and addresses the constitutional soil to prevent recurrence. Together, they form a holistic approach to patient care.
Scope of Homoeopathy in Surgical Practice
1. Pre-Operative Utility
Homoeopathic medicines help establish physiological equilibrium, emotional calm, and reduced susceptibility before surgery:
• Managing anxiety: Aconitum, Gelsemium, Argentum nitricum.
• Reducing shock probability: Arnica Montana.
• Addressing bleeding tendencies: Phosphorus, Hamamelis.
• Strengthening vitality in chronic disease states.
2. Intra-Operative Considerations
Although remedies are not administered during the surgical act, preoperative Homoeopathic therapy helps minimize:
• Excessive bleeding (Phosphorus, Arnica).
• Shock and collapse (Carbo vegetabilis).
• Increased anaesthetic sensitivity (Phosphorus).
3. Post-Operative Utility
This is the most documented and clinically successful area:
• Pain management: Hypericum, Arnica, Mag phosphoricum.
• Wound healing acceleration: Calendula, Graphites, Calc sulph.
• Suppuration control: Hepar sulph, Merc sol, Silicea .
• Fracture recovery: Symphytum enhances callus formation.
• Haemorrhage control: Hamamelis, Ipecac, Secale.
• Prevention of adhesions: Thiosinaminum.
• Scar sensitivity improvement: Fluoric acid.
Materia Medica Insights for Surgical Applications
1) Arnica Montana
Indicated for trauma, shock, bruising, surgical soreness. Clinical evidence supports improved postoperative recovery.
2) Calendula officinalis
Promotes rapid granulation, prevents sepsis, and improves incision healing.
3) Hypericum perforatum
Indicated for intense nerve-rich pain after surgery, especially spinal or digital injuries.
4)Staphysagria
Useful for clean incised wounds, postoperative irritation from catheters and surgical manipulation.
5)Symphytum officinale
Stimulates osteoblast activity and improves fracture union.
6) Hepar sulphuris calcareum
Controls suppuration and prevents abscess formation.
7) Silicea terra
Effective in chronic fistulae, recurrent abscesses, and delayed healing.
8) Bellis perennis
Acts deeply on muscular tissues, excellent for abdominal and pelvic surgeries.
9) Hamamelis virginiana
Reduces venous haemorrhage and postoperative bleeding.
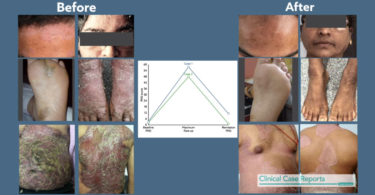
Clinical Evidence
Multiple studies indicate benefits of Homoeopathy in surgical contexts: • Faster wound healing with Calendula ointment.
• Reduced postoperative pain with Arnica and Hypericum.
• Improved bone healing with Symphytum.
• Lower infection rates and more efficient healing with individualized Homoeopathic treatment.
• Enhanced global well-being in postoperative cancer patients receiving adjunctive Homoeopathy.
Ethical Considerations and Limitations
Homoeopathy cannot replace surgery, nor can it manage conditions requiring immediate mechanical intervention such as perforation, acute obstruction, torsion, or severe trauma. Ethical integration requires clear referral criteria, informed consent, and collaborative practice with surgeons. Homoeopathy provides supportive care—not a replacement for operative necessity.
Future Perspectives
1. Integrative Surgical Units
Including Homoeopathic consultants in surgical departments can optimize recovery protocols.
2. Standardized Peri-Operative Guidelines
Research-based protocols will enhance acceptance and reproducibility.
3. Advanced Research
RCTs, mechanistic models, and biomarker studies on wound healing and inflammation. 4. Curriculum Enhancement
Incorporation of surgical therapeutics in postgraduate Homoeopathic education and clinical postings.
Discussion
Homoeopathy stands today as a dynamic, indispensable, and increasingly respected partner in the landscape of surgical care. While surgery masterfully resolves structural, mechanical, and life-saving challenges, Homoeopathy elevates the healing journey by working on the deeper,
dynamic, and constitutional levels of the human organism. Together, these two disciplines form a powerful therapeutic alliance—one that restores anatomical integrity while simultaneously strengthening vitality, resilience, and long-term wellbeing. The peri-operative value of Homoeopathy is both clinically profound and therapeutically elegant. Remedies like Arnica for trauma and surgical shock, Staphysagria for incised wounds, Hypericum for nerve-rich injuries, Ruta for soft-tissue trauma, and Calendula for rapid granulation exemplify the system’s ability to produce cleaner wounds, smoother recoveries, and reduced postoperative distress. Moreover, constitutional prescribing—based on totality and miasmatic depth—plays a pivotal role in chronic surgical conditions such as fistulae, abscesses, hemorrhoids, and recurrent suppurative lesions. This deeper approach not only addresses the presenting pathology but helps prevent recurrence by modifying underlying susceptibility.
The wisdom of stalwarts—Hahnemann’s clarity, Kent’s philosophy, Boger’s precision, Ludlam’s surgical brilliance—consistently reinforces that Homoeopathy and surgery are complementary sciences, not competing domains. Surgery corrects what is mechanically displaced; Homoeopathy restores what is dynamically disturbed.
In the era of integrative medicine, patients increasingly seek healing that is gentle, holistic, personalized, and scientifically grounded. Homoeopathy answers this call by enhancing surgical outcomes, reducing pharmacological load, minimizing complications, and ensuring a faster, cleaner, and more harmonious recovery.
Thus, Homoeopathy occupies a vital and future-oriented role in surgical practice—bringing together precision, gentleness, and constitutional healing. Its contribution is not merely
supportive but transformative, redefining recovery and promoting a future where surgery and Homoeopathy work hand in hand to achieve complete healing.
References
Hahnemann S. Organon of Medicine. 6th ed. New Delhi: B. Jain Publishers; 1994.
2. Boericke W. Boericke’s New Manual of Homeopathic Materia Medica with Repertory. New Delhi: B. Jain Publishers; 2010.
3. Kent JT. Lectures on Homoeopathic Philosophy. New Delhi: B. Jain Publishers; 2002.
4. Clarke JH. A Dictionary of Practical Materia Medica. New Delhi: B. Jain Publishers; 1997.
5. Allen HC. Keynotes and Characteristics with Comparisons. New Delhi: B. Jain Publishers; 2009.
6. Close S. The Genius of Homoeopathy. New Delhi: B. Jain Publishers; 2010. 7. Farrington EA. Clinical Materia Medica. New Delhi: B. Jain Publishers; 1992.
8. Tyler ML. Homoeopathic Drug Pictures. New Delhi: B. Jain Publishers; 2004.
9. Helmuth CM. System of Surgery. New York: Boericke & Tafel; 1888. 10. Ludlam RE. A Textbook of Homoeopathic Therapeutics. Chicago: Gross & Delbridge; 1896.
11. Younkers HE. Surgical Therapeutics and Materia Medica. Philadelphia: Boericke & Tafel; 1900.
12. Master FJ. Homeopathic Principles and Practice. Mumbai: FJ Publications; 2018.
13. Banerjea SK. Miasmatic Prescribing. Kolkata: Miasmatic Research Foundation; 2010.
14. Vithoulkas G. The role of homeopathy in modern medicine. Homeopathy. 2000.
Co-Author – Dr Santosh Anand Mishra — PG Scholar, RBTS Government Homoeopathic Medical College and Hospital, Muzaffarpur, Bihar