
Abstract: Dengue has been a major health concern for long period and seem to have increase in the number of cases in recent years. The viral infection spread by mosquito bite and have potential to create life threatening consequences. Modern medicine deal fever and debility with NSAIDs and aspirin but many drugs are restricted on account of pathophysiology of dengue hemorrhage. Dengue itself has its major symptom spectrum, treatment should be promising and of minimal side effect here homoeopathy comes in role. This article talks about homoeopathic remedy from compositae family with fast recovery and no side effect of dengue treatment whatsoever.
Keywords: Dengue, compositae family, pyrexia, homoeopathic management, dengue shock syndrome
Abbreviations: RNA- ribonucleic acid , WHO- world health organisation , NSAIDs- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, ESR- erythrocyte sedimentation rate, BP – blood pressure
Introduction- Dengue virus is caused by the RNA type distinctive subgroup of the 4 dengue virus. It is basically manifested in broad three different pattern. According to WHO classification of dengue (2009), it is categorised as: 1
1)Dengue with No or less warning signs.
2) Dengue with warning sign.
3) Severe dengue.
I) Dengue no or less warning signs:
- Probable dengue
- Live in/travel to dengue endemic areas. Fever and 2 of the following:
- Tourniquet test positive
- Rash
- Aches and pains
- Nausea, vomiting
- Any warning sign
and
- Supportive serology
Or
- Occurrence at the same location and time as other confirmed dengue cases 1
II) Warning signs:
- Abdominal pain and tenderness
- Persistent vomiting -Clinical fluid accumulation
- Mucosal bleed
- Lethargy, restlessness
- Liver enlargement > 2 cm
- Laboratory: increase in hematocrit
- concurrent with rapid decrease in platelet count
- [requiring strict observation and medical intervention.] 1
III) Severe dengue:
- Any of the followings:
- Severe plasma leakage leading to shock or respiratory distress.
- Severe bleeding as evaluated by clinicians.
- Severe organ involvement
- Liver
- CNS: impaired consciousness -Heart and other organs. 1
Clinical features of dengue are classified as below:
1) Febrile phase:
- High-grade fever 2-7 days.
- Facial flushing, skin erythema, body ache, myalgia, arthralgia, severe back ache(“breakbone” fever), retro-orbital pain and headache.
- Sore throat, injected pharynx and conjunctival injection
- Anorexia, nausea and vomiting.
- Seizures in children.
- 3-4 days for 2 days and is followed by return of fever “saddleback fever”
- Tenderness upon pressure on the eyeball.
- A positive tourniquet test may be present.
- Petechiae and mucosal membrane bleeding.
- Liver is often enlarged and tender.
- Progressive decrease in total white cell count. 2,3
2) Critical phase:
- Time of defervescence of fever, an increase in capillary permeability along with increasing haematocrit levels may occur. Beginning of critical phase. Reflects severity of plasma leakage.
- Significant plasma leakage usually lasts for 24-48 hours.
- Pleural effusion and ascites may be detectable.
- Shock occurs when critical volume of plasma is lost through leakage, warning signs.
- Body temperature may be subnormal when shock occurs.
- With prolonged shock, organ hypoperfusion result in progressive organ impairment, metabolic acidosis and dic this in turns leads to severe hemorrhage causing the hematocrit to decrease in severe shock
- Leucopaenia, leucocytosis may occur in patients with severe bleeding. 2,3
3) Recovery phase:
- If the patient survives the 24-48 hours critical phase a gradual reabsorption of extravascular fluid takes place in the following 48-72 hours
- General well-being improves appetite returns, haemodynamic status stabilises.
- Bradycardia
- Respiratory distress from massive pleural effusion and ascites will occur at any time if excessive intravenous fluids have been administered.
- White blood cell count usually starts to rise soon after defervescence but recovery of platelet count is typically later than that of white blood cell count. 2,3
Scope of homoeopathy in dengue
Though modern medicine treat acute emergency of acute leucocytopaenia ,there is no definitive treatment except platelet transfusion which highly depend upon its availability also has its own health hazard, this whole complex process is can be avoided with homoeopathic treatment. Homoeopathic medicine can be used according to therapeutic at different stages such as Carica papaya helps to increase the platelet count. Homoeopathy can combat fever in all stages with indicated similimum to avoid the further consequences and bring back patient back in its harmony in short period.
Compositae family-
Also called as the daisy and Asteraceae family.
They are used as medicines by human since long time for different means mainly considering injury, fever and convulsions.
Eupatorium belonging to the same family manifest some important clinical features and symptoms mention below.4
The leading characteristic of Eupatorium perfoliatum
- Violent aching, bone breaking pains.
- Muscles of chest, back and limbs feel bruised, sore aching.
- It affects the liver producing bilious effects.
- Patient is restless, chilly and nauseated
- Colds, influenza.
- Dengue.
Dropsy of legs, feet and ankles. - Thirst or nausea, then violent shaking chill; begins in the small of the back. Bitter vomiting after chill or during heat.
- Burning heat.
- Sweat; relieves all the symptoms except the headache.
- Sweat scanty. 5
CASE REPORT- 50-year-old female who was suffering from pyrexia had complaints of headache, body ache with cough and nausea, which had progressed gradually over 7 days. Initially, symptoms were mild, patient tried home remedies for first 3-4 days, then patient started suffering from fever so patient took paracetamol 650 once daily for 3 days but it didn’t give any significant relief to patient as it temporarily brought down fever for a short span.
History of presenting complaints- all the complaints started gradually over a week after patient travelled to a nearby hill station in rainy weather
Physical and mental generals-The patient was chilly. Patient observed febrile episodes which were uncertainly periodic. Moaning during peak of fever. Patient was restless during fever and was worried about if she will have weakness or will have to rest for weeks. She was having headache and aching sensation in extremities. All her symptoms became better after perspiration except headache. Also. there was marked desire for cold water.
General physical examination- height – 5’2”, weight – 55kgs. anaemia – nil, jaundice – nil, cyanosis –nil, generalised lymphadenopathy – nil, pulse –83 / min, temperature101˚ F, respiratory rate -18 / min, BP -130 /82 mm Hg. Tongue – dry and cracked, nails yellow.
Systemic examination- respiratory, gastro-intestinal, locomotor and nervous system are found to be normal
Therapeutic intervention- Detailed case taking was done as per Hahnemannian guidelines of case taking given in Organon of medicine followed by analysis and evaluation of the symptoms done. Totality was erected and prescription was done on the basis of striking mental and physical general. The case contained characteristic, qualified mental symptoms and physical generals; hence, Kent’s approach was selected for this case. 6
Analysis and evaluation by Kent’s Repertory–
| symptoms | Location | Sensation | Modalities | Conc omit tant | Totality of symptoms |
| 1.Mind – restless heat during | >perspiration | Mental general | |||
| 2.Mind – fear suffering | >perspiration | Mental general | |||
| 3.Mind- Moaning during fever | >perspiration | Mental general | |||
| 4.Fever- changing, paroxysms | >perspiration | General symptoms | |||
| 5.Generals – food and drinks-cold drink- desire | >perspiration | Mental general | |||
| 6.Perspiration – symptoms – while sweating, amel., except the headache, which is made worse | <perspiration | Mental general | |||
| 7.Extremities – pain – aching | Extremities | >perspiration | Mental general | ||
| 8.Head – pain – accompani ed by – fever | Head | >perspiration | General symptoms | ||
| 9.stomach-nausea-fever-during-agg | GIT | aching | >perspiration | Particular symptoms |
Repertorial totality 7
- Mind – restless heat during
- Mind – fear suffering
- Mind- Moaning during fever
- Fever- changing, paroxysms
- Generals – food and drinks-cold drink- desire
- Perspiration – symptoms – while sweating, amel., except the headache, which is made worse
- Extremities – pain – aching
- Head – pain – accompanied by – fever
- Stomach-nausea-fever-during-agg
After repertorisation with the Synthesis repertory, the top five remedies as per their numerical totality were as follows:
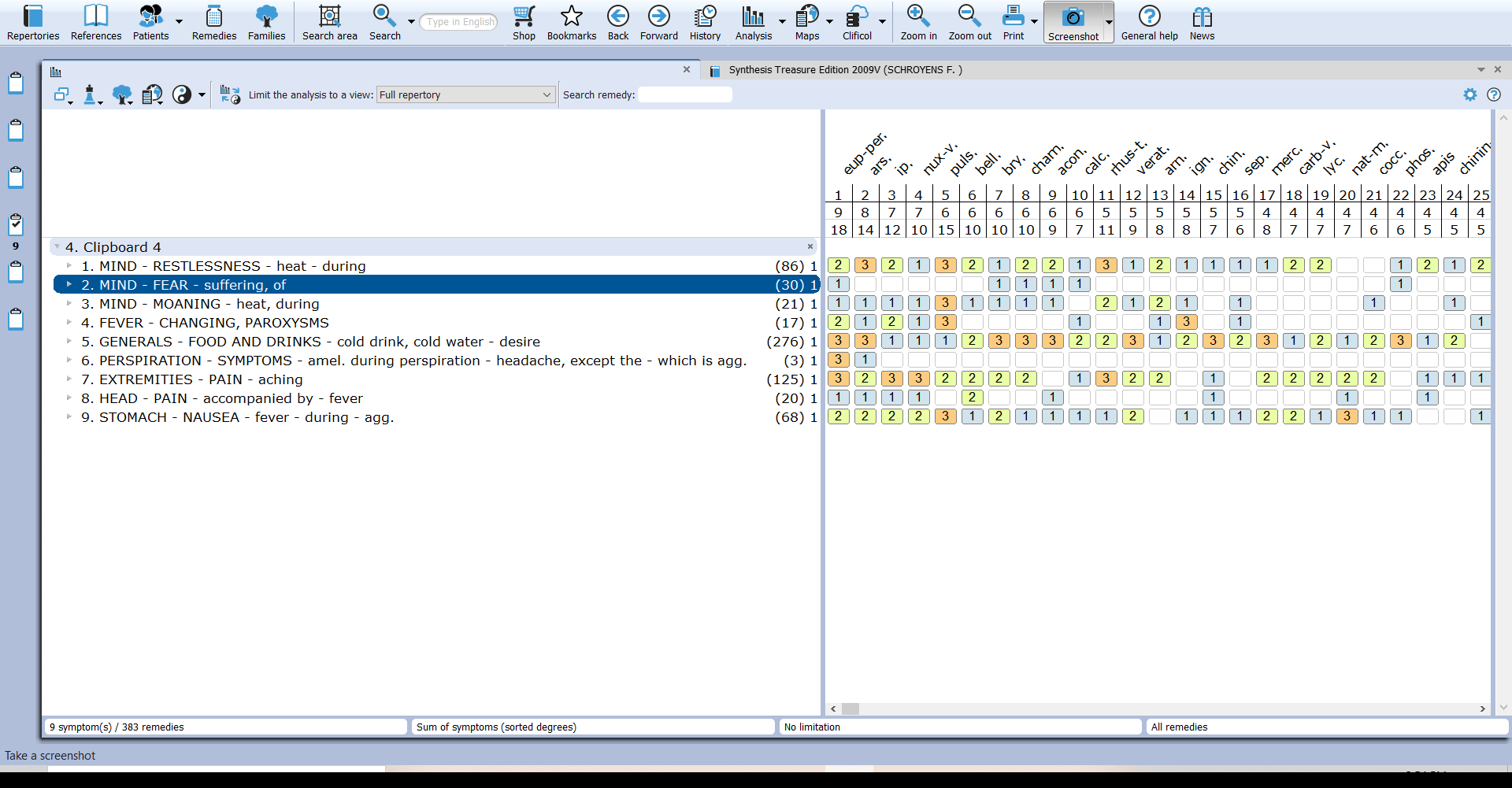
Selection of remedy- After repertorial analysis, strong indication of symptom similarity and while confirming the remedy from materia medica, it was mentioned under Eupatorium perfoliatum generalities in Phatak’s repertory that it can be useful in dengue fever , even in Clarke’s materia medica, it is mentioned that bone pain due to any influenza or malaria can be cured by Eupatorium perfoliatum. Considering the above point, Eupatorium perfoliatum was confirmed.8,9
Susceptibility, posology and repetition- The disease manifestation, in this case, was acute and showed a gradual progress with no characteristic structural changes. The patient showed marked sensitivity at the mental level with prominent dispositional and mental expressions, so the sensitivity was high. The pathology was structurally reversible and the miasm was acute miasm of recurrent type10. Hence, the susceptibility of the patient was moderate to high. Thus, 200 potency was selected and repeated infrequently.6,7,10,11
Prescription-The patient was prescribed Eupatorium perfoliatum 200, three dose 6 hourly with placebo 4 pills three times a day. follow-up after 2 days. Advised investigation to confirm the diagnosis.
| Follow up | Complaint | Interpretation | Prescription |
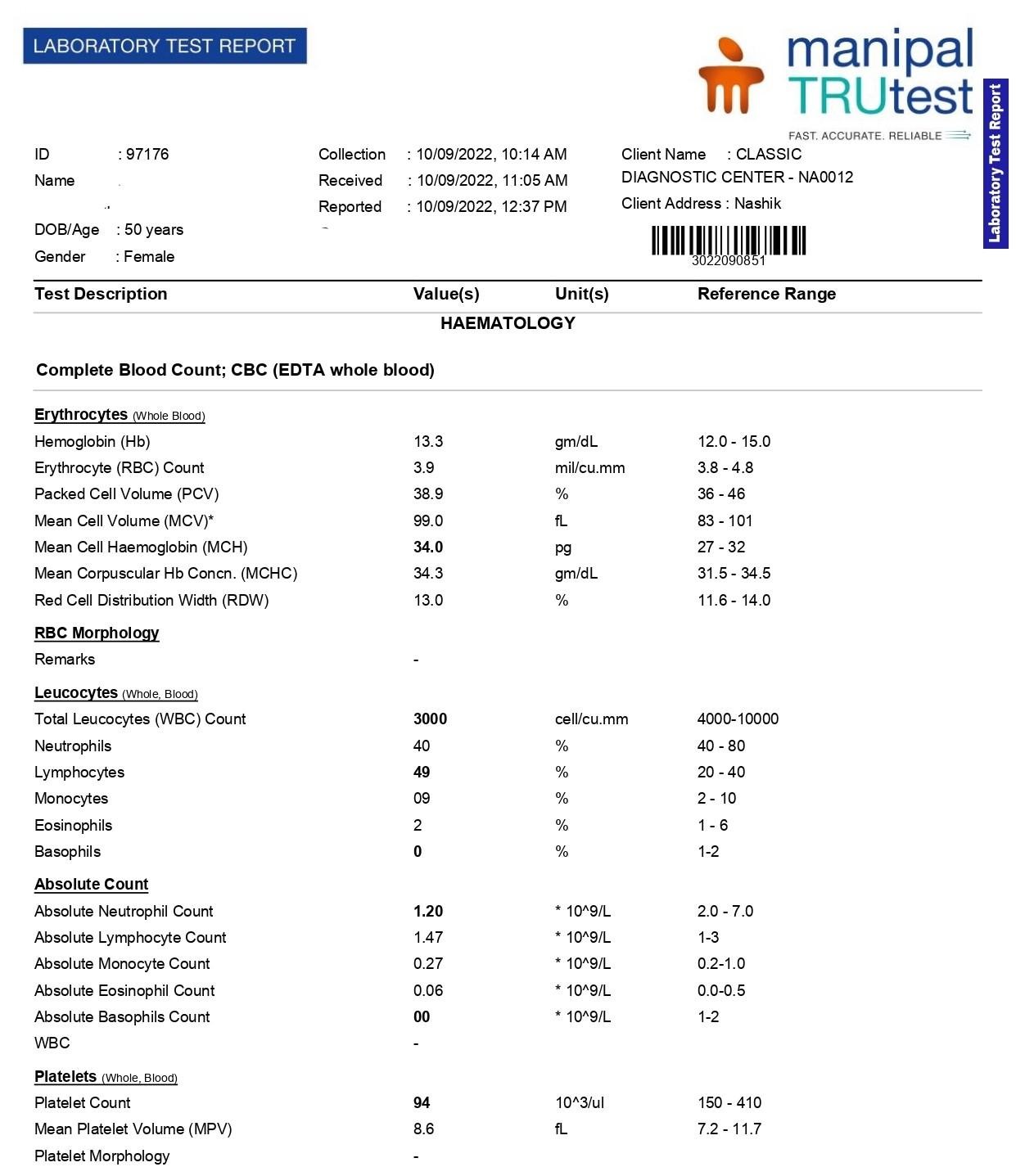
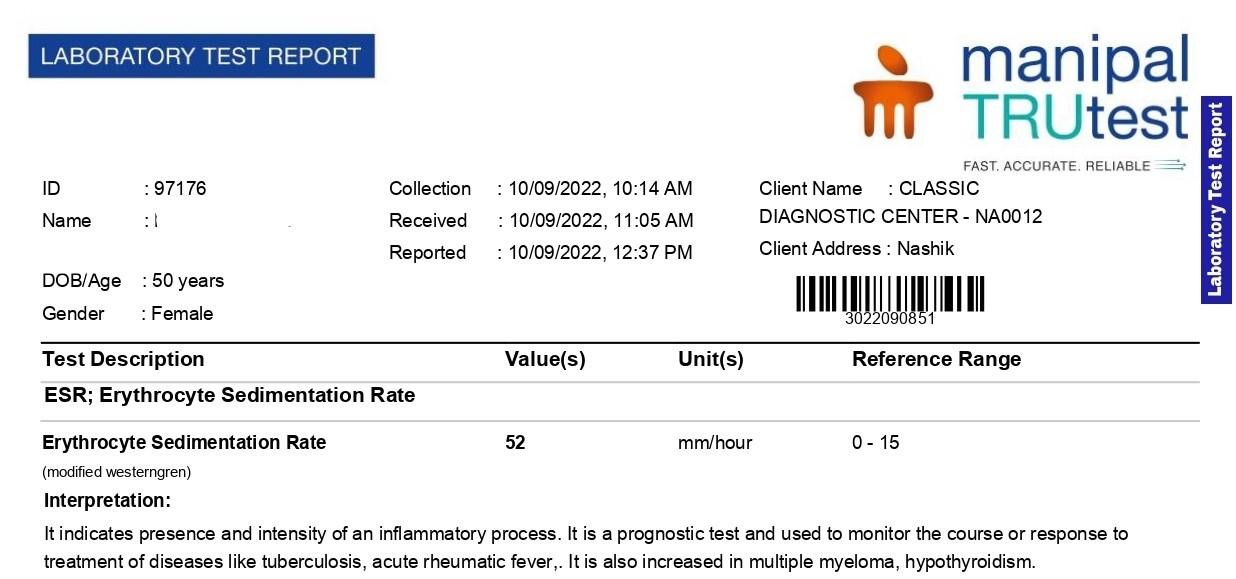
| 1st follow up 10 sept 2022 | Patient generally felt better as restlessness of mind decreased. Fever persistent with less severity of extremities pain. headache persistent Diagnosed clinically dengue fever with increased ESR i.e.52 and decreased platelets 92000 Decreased | Improvement | Placebo 3 doses 6 hourly prescribed |
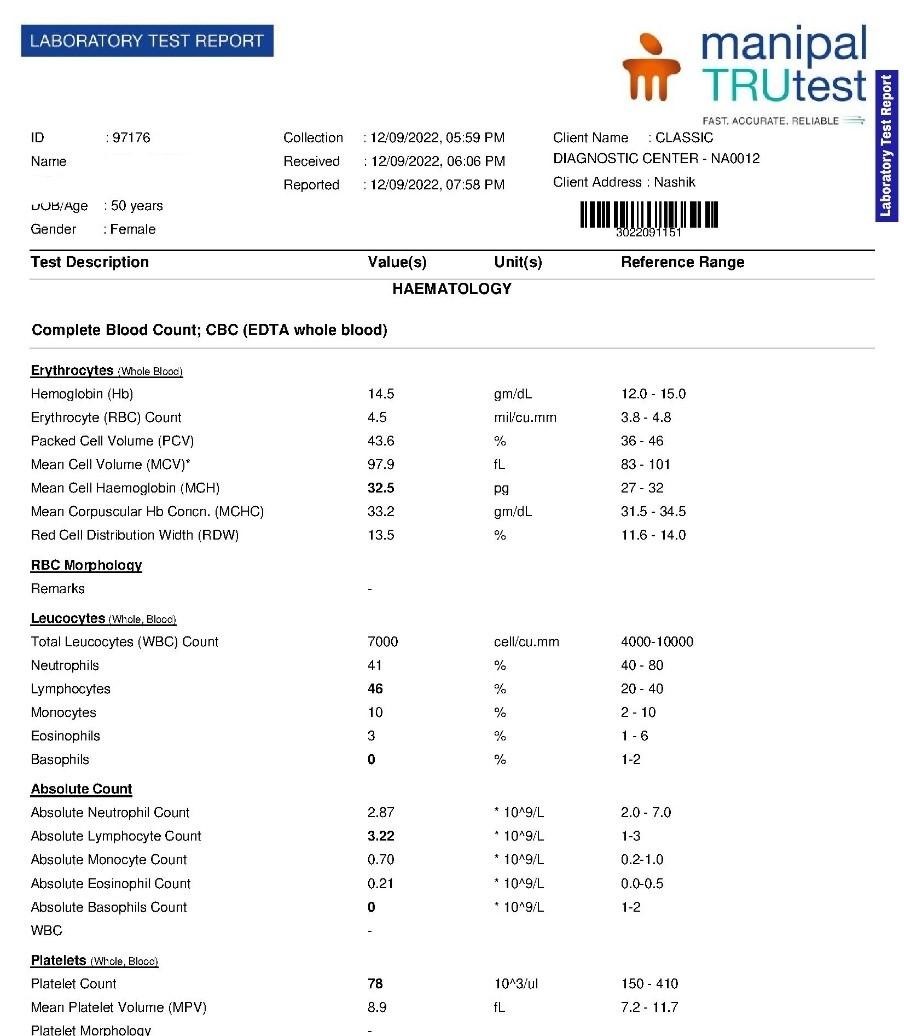
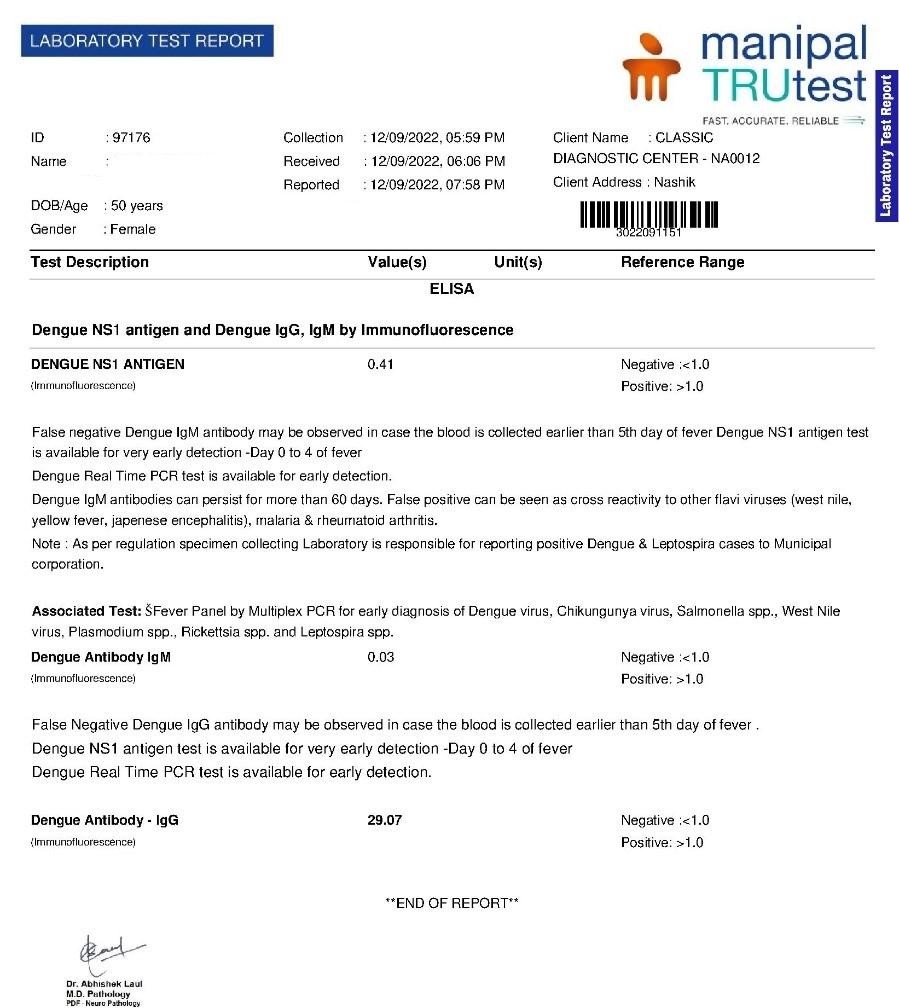
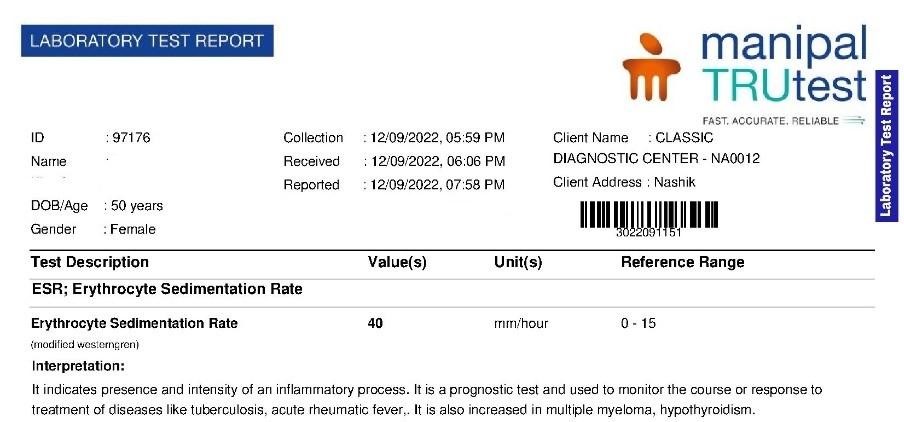
| 2nd follow up 12 sept 2022 | Patient generally better but reports shows decreased platelet count 78000 along with decreased ESR 40 Fever and headache still persistent on irregular basis | Improvement in platelet but ESR decreased. | Eupatorium perfoliatum 1M one dose with placebo 4 pills three times a day |
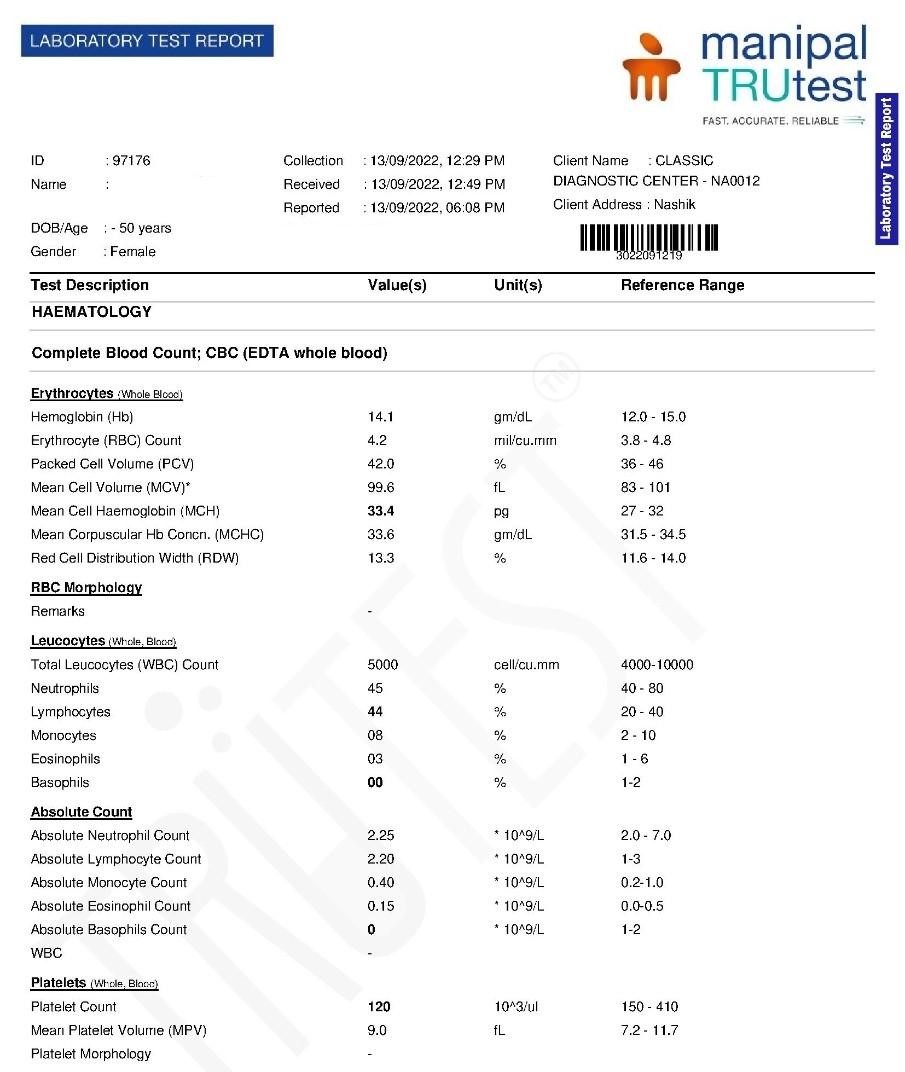
| 3rd follow up 13 sept 2022 | Platelet count increased 12000, fever subsided with generally better feeling less extremities pain , headache persistent with less severity . | Improvement. | Placebo 4 pills three times a day |
| 4th follow up 14 sept 2022 | Better generally with no headache and fever | Improvement | Placebo 4 pills three times a day for 5 days |
Change of potency:
The first potency aroused the action but ceased after a while this can be interpreted as the remedy is correction but needs higher potency. 12
Blood Reports of 10th September 2022:
Blood reports (12th September 2022)
Blood reports (13th September 2022)
Management and outcome –
Patient was generally advised to:
- Have well-balanced diet, with emphasis on fresh fruits such as kiwi, peach, pineapple.
- Drink plenty of fluids.
- Cold compress may be applied to the head, in case the temperature rise above 1030F.13
The duration of treatment was around 6-7 days after that patient felt better both mentally and physically and discontinued the treatment as her reports came normal.
Conclusion- Homoeopathy is useful in treating the cases of infectious fever when prescribed on the basis of individualisation. More evidence based study may be needed to validate the result. The authentic materia medica and literatures of compositae family shows overall god result in the cases of fever with overall beated broken painful feelings and gradual onset.
Acknowledgement– The author is thankful to all the reviewers for reviewing and editing article to encourage for sharing experiences and knowledge in field of research.
Declaration of patient consent- The authors certify that they have obtained appropriate patient consent form. In the form, the patient has given her consent for her clinical information to be reported in the journal. The patient understands that her name and initials will not be published and due efforts will be made to conceal her identity, but anonymity cannot be guaranteed.
REFERENCES:
- World Health Organization (https://www.who.int/)
- Mathew G. Aggarwal P. Medicine: Prep Manual for Undergraduates. Elsevier. 2015.
- Dengue. How to best classify it: clinical infectious disease. 2011, Sept 15, 53 (6): 563- 567. Srikrantkhachorn A.
- Patil, J. Group Study in Homoeopathic Materia Medica.2006.
- Phatak S R, Materia Medica Of Homoeopathic Medicines B.jain publisher.1999
- Hahnemann,S. Organon of medicine.6.B.jain publisher.1906.
- Radar Opus Homoeopathic Software (www.radaropus.com)
- Phatak,S. Materia Medica of Homoeopathic medicines.2.1999.
- Clarke,J. A dictionary of practical materia medica.3.1925.
- Das,A. A treatise on materia medica. 2016
- Mandal, M. A textbook of homoeopathic pharmacy. New central book agency.1994.
- Dhawale,M. principles and practice of Homoeopathy. Narayan verlag.1967.
- Bakhru, HK. The complete handbook of nature cure.5.jaico publishing house.1991.





