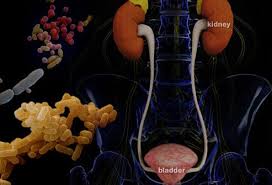
 Introduction
Introduction
The female is more victim of the infection than the male. When the lower urinary tract including urinary bladder is infected it is called cystitis; when the upper urinary tract including kidneys is infected it is called the pyelonephritis. Both are called the urinary tract infection (UTI). In lower urinary tract infection there is pain and frequent urination. There may be too much urging to urinate. Fever and flank pain are common in upper urinary tract infection; sometimes, symptoms of a lower UTI may be associated. In most of the cases the bacteria Escherichia coli is the causative agent.
Women are infected with the bacteria frequently; in the pregnancy period is more common. The recurrence of the infection is usual. Risk factors include female anatomy, sexual intercourse and family history. Diagnosis in young healthy women can be based on symptoms alone. In many cases the diagnosis can be difficult, because bacteria may be present without producing symptoms.
Urinary tract infections are easily treatable with some homeopathic medicines. In complicated cases, longer course of treatment may be needed. Sometimes, the infection may come due to the presence of other bacteria and it prolongs the course of infection. In women, urinary tract infections are the most common form of bacterial infection.
Urinary tract infections and the similar diseases have been described in literature since ancient times with the first documented description in the Ebers Papyrus dated to c. 1550 BC. The Egyptian physicians described it as sending forth heat from the bladder. Effective treatment did occur after the discovery of homeopathy medicine and its application after 1810. Before that some types of herbs, bloodletting and rest were in vogue.
Aetiology
A predisposition for bladder infections may run in families. Other risk factors include diabetes, non-circumcision and prostatomegaly. In children UTIs are associated with vesicoureteral reflux constipation.
Escherichia coli are the cause of 80–85% of urinary tract infections. In 5-10 percent of cases Staphylococcus saprophyticus is the cause. Viral or fungal infection is very rare. Bacteria like Klebsiella, Proteus, Pseudomonas, and Enterobactera may produce UTI. UTI due to the infection of Staphylococcus aureus generally occur secondary to the blood-borne infection.
Sexual activity of the women is one of the causes of bladder infection in 75-90% cases. Honeymoon cystitis is common during early marriage period. Spermicide use increases the risk of UTIs.
Women are more prone to UTIs, because in females, the urethra is much shorter and closer to the anus. At menopause, the infection can be more due to the loss of protective vaginal flora. Urinary catheter use increases the risk for urinary tract infections.
Symptom summary
The most common symptoms are burning with urination. Frequent urination but no vaginal discharge and significant pain are noticed. Symptoms vary from mild to severe form and in healthy women they last an average of six days. In some cases pain above the pubic bone or in the lower back may be present. In pyelonephritis, there are flank pain, fever, nausea and vomiting. Urine may appear bloody or contain visible pyuria in a low percentage of cases.
In young children, the only symptom of UTI may be a fever. When the cause of the fever is not known in case of females under the age of two or uncircumcised males less than a year a culture of the urine is recommended. In Infantile attack they take poor quantity of food, vomit, sleep more, or show signs of jaundice. In older children, new onset of urinary incontinence may occur.
Elderly people present vague symptoms with incontinence, a change in mental status and exhaustion.
Urine contains pus mixed with RBC.
Pathogenesis
Primarily the urinary tract infection producing bacteria typically enter the urinary bladder via the urethra. Infections may also take place via the blood or lymph. The bacteria are usually transmitted to the urethra from the bowel. Females are at greater risk due to their special anatomical configuration. After gaining entry to the bladder, the E. coli are able to attach to the bladder wall and form a biofilm. The film resists the body’s immune response.
Prevention
Urinating immediately after intercourse, personal hygiene methods used after urinating or defecating, or a bath may be helpful. Urethral wash with plain water is also suggested.
Recurrent infection needs a chronic treatment with the indicated anti-miasmatic medicine. Sexual Intercourse related infection can be easily controlled by the use of some specific homeopathic medicine like Medorrhinum, Sabadilla, Staphisagria etc. In post-menopausal period infection topical vaginal estrogen has been found to be effective in reducing the recurrence.
Routine circumcision in male child prevents the UTI in many cases.
Diagnosis
Multiple rod-shaped bacteria are seen between white blood cells.
In most cases a diagnosis may be made and treatment given based on symptoms alone. In complicated cases it may be useful to confirm the diagnosis via urinalysis, looking for the presence of urinary nitrites, white blood cells , or leukocyte esterase. Urine culture is deemed positive if it shows a bacterial colony count of greater than or equal to 103 colony-forming units per mL of a typical urinary tract organism. When symptoms can be vague and without reliable tests for urinary tract infections, diagnosis can be difficult in the elderly person.
Classification
Lower urinary infection generally occurs in the urinary bladder. It is called the bladder infection or cystitis. Likewise the upper urinary infection occurs in the kidneys and it is called the pyelonephritis. If the urine contains significant bacteria but there are no symptoms, the condition is known as asymptomatic bacteriuria. If a urinary tract infection involves the upper tract, and the person is diabetic it is complicated. If a woman is healthy and premenopausal it is considered uncomplicated. In paediatric cases when a urinary tract infection is associated with a fever, it is usually considered a case of upper urinary tract infection.
To make the proper diagnosis of a urinary tract infection in children, a positive urinary culture is required. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends renal ultrasound and voiding cystourethrogram in all children less than two years of age, who have had a urinary tract infection.
Sometimes, Chlamydia trachomatis or Neisseria gonorrheae infection may be the cause of cervicitiis, vaginitis and UTI. Vaginitis may also be due to a yeast infection. Interstitial cystitis may be considered for people, who experience multiple episodes of UTI symptoms with negative urine culture report.
Epidemiology
UTIs are the most frequent bacterial infection in women. They occur most frequently between the ages of 16 to 35 years. The recurrence is common. UTIs occur four times more in females than males. Cystitis is more common than Pyelonephritis. Asymptomatic UTI is more than 50 percents. Rates of asymptomatic bacteria in the urine among men over 75 are between the ages of 7-10%.
The UTIs may affect 10% of people during childhood. Among children urinary tract infections are the most common in uncircumcised males, followed by females less than one year. In a group of children with a fever, ranging in age between birth and two years, 02 to 20% were diagnosed with UTI.
Attack in Pregnancy period
Urinary tract infections are more common in the period of pregnancy. At the period the risk of kidney infection is too much usual. During pregnancy, high progesterone levels elevate the risk of decreased muscle tone of the ureters and bladder. It leads to a greater chance of reflux, where urine flows back up the ureters and towards the kidneys. Pregnant women do not have an increased risk of asymptomatic bacteriuria. If bacteria in urine are present they do have a 25-40 percent risk of a kidney infection. If the bacteria are present in the urine without any dominant symptoms the treatment should also be recommended. It is also evident that the body starts developing symptoms as soon as the bacteria are present in the system. A kidney infection during pregnancy may result premature birth or pre-eclampsia.
Treatment
There are lots of homeopathic medicines to combat the suffering of UTI. If the proper medicine is prescribed the course of infection is too much less and the within 48 or 72 hours the condition is improved and the patients feel better or it is totally cured.
In acute cases, the medicine acts in a speedy, calm and lasting way. In chronic and complicated cases it takes some more time but within a week it is corrected in a good method. Pyelonephritis with vomiting needs Apocyanum 6CH, 8 doses every 2 hours. In Upper urinary tract infection with brain complaints Plumbum met 6CH, 4 doses is useful. Cystitis with female genitalia infection, the medicine is Canth 6CH, 4 doses. Acute cystitis is rapidly controlled by Mezerium 30CH, 2 doses. Cystitis after first intercourse needs Staph 6CH, 4 doses. In hemorrhagic cystitis it needs Canth 6CH, 4 doses. UTI with violent pain and clear blood is the case of Nit. ac 6CH, 4 doses. UTI in the period of pregnancy needs Eupat perf 6CH, 4 doses. Millifolium 6CH, 6 doses is enough to control the cystitis with pus like discharge after lithotomy. If the cystitis is developed after the attack of scarlet fever it is Cantharis 6CH. Cystitis with throbbing all over is the unique symptom of Sabina 6CH.
A Case
One of our relatives consulted me for a lady suffering from some urinary problems. She was pregnant and it was in advanced stage. The party was too careful to take the treatment at the stage. Everyone was too much worried, because the pregnancy had been taken its shape after about nine years since the marriage. Once she had an abortion at the third month. It happened at the second years of marriage. Since then she kept getting treatment after treatment. In the long run she was pregnant. Automatically, everyone was cautious and alert. As I was at that time a learner and asked the party to bring the patient to my newly opened clinic. It was in the year 1981.
Next day, the patient came with her mother-in-law. She was 25 years old. She complained that she had pain in the lower abdomen and urethra during the passage of urine. Frequent urination. She was scared of going to the toilet. It was a horrible circumstance to her. Sometimes, she tried to avoid the urination. Pain referred to the whole of abdomen. She had headache in the afternoon hours. The patient was always anxious, as she thought she was watched by all the people. Everybody was interested to her and was too much observant to the patient. On the notion she avoided going anywhere else.
Sometimes, the urinary infection is unresponsive to different types of medicines. Some antibiotics become resistant. In pregnancy period the doctor are hesitant to prescribe the most powerful antibiotics. So the infection remains for the prolong period of time.
The woman had muttering delirium. Sometimes, it was thought that the attack was due to influence of spectre. The patient always thought she would have a gay baby, as once a mad man foretold her she would have a gay baby, when she denied him to donate alms. She was scared of the matter.
There were 5 or 6 patients in my chamber and all were ahead of the lady. So, it took a long time to attend her and she thought she was away from home for a long time and became restless.
Stool and perspiration were offensive. She had aversion to bread and tea.
The pulse and the respiration rate were almost normal. The blood pressure remained a little bit high. Once the doctor prescribed her the anti hypertensive drug. The family his was full of Diabetes M type11. Her husband once had urinary infection. His blood for VDRL and HIV 1 & 11 were normal.
The woman did not tolerate cold in any form. Sometimes, bathing in the nearby pond causes cough and cold.
Medicine selection and the important rubrics:
Fear, superstitious.
Delusion, home, he is away from.
Delusion, watched, that she is being.
Stomach, desire, bread.
Cold in general aggravation.
Bathing dread of.
Only one medicine came to the light and it was RHUS TOXICODENDRON. I prescribed the medicine in 12CH /8 doses in sugar of milk. Four times a day for two days. The patient took the medicine and within a week she was cured.
Discussion
Urinary tract infection is a common problem in male female both. Sometimes it takes short time sometimes long. In homeopathic treatment it is easily controllable. Studies show the cure rate is significant. In the above case the medicine is prescribed on the basis of mental and physical symptoms. It is really bizarre that all the prescriptions are made on the cardinal symptoms of the patient. The pathological data are useful to another matter, not in the selection of medicine.
How bacteria and virus are inactive in the body after taking homeopathic medicine is still now the mystery. Scientific studies are underway to unfold the Nature’s hidden phenomenon.
A group of homeopathic medicines are potent enough to control the disease and its many complications. The lower potency is more useful in the acute and chronic cases of UTI.
At the time of pregnancy UTI is the common infection in most of the females. In the cases the indicated homeopathic medicine cures the patient from the root and it is in a shortest time.
References
Anthony S. Fauci et al. Harrison’s Principles of Internal medicine. Mc Graw Hill Companies, Inc. 17th edition 2008, 1820-26.
Colgan, R; Williams, M, Johnson, JR. Diagnosis and treatment of acute pyelonephritis in women. American family physician 2011. 84 (5): 519–26.
Colgan, R; Williams, M. Diagnosis and treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis. American family physician 2011. 84 (7): 771–6.
Dielubanza, EJ; Schaeffer. Urinary tract infections in women. The Medical clinics of North America 2011. 95 (1): 27–41.
Gupta, K; Hooton, TM, Naber, KG, Wullt, B, Colgan, R, Miller, LG, Moran, GJ, Nicolle, LE, Raz, R, Schaeffer, AJ, Soper, DE, Infectious Diseases Society of, America, European Society for Microbiology and Infectious, Diseases (2011-03-01). “International clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis in women: A 2010 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the European Society for Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. Clinical infectious diseases: an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America 52 (5): e103–20.
Hering C. Condensed Materia Medica. M Bhattacharyya & Company, Calcutta. 1st Indian Edition 1962. 832-40.
Kent J T. Repertory of the homeopathic materia medica. Seth Dey & Co., Calcutta 1, 1974.
Nicholas A B et al. Davidson’s Principles and Practice of Medicine, Elsevier 2006, Philadelphia, Pa. 20th edition, 467-70.
Nicolle LE. Uncomplicated urinary tract infection in adults including uncomplicated pyelonephritis. Urol Clin North Am 35 (1): 1–12.
Raynor, MC; Carson CC. Urinary infections in men. The Medical clinics of North America 2011, 95 (1): 43–54.
Rossi, R; Porta, S, Canovi, B. Overview on cranberry and urinary tract infections in females. Journal of Clinical Gastroenterology 2010. 44 Suppl 1: S61–2.
Salo, J; Ikäheimo, R, Tapiainen, T, Uhari, M (2011 Nov). “Childhood urinary tract infections as a cause of chronic kidney disease.” Pediatrics 128 (5): 840–7.
Schroyens Frederik, Synthesis, Homeopathic Book Publishers 1998, London, Edition 7.1, ISBN 1-902575-00-8.
Author: Dr Md Azmal Hossain B Sc, D M S (Cal).
Searching Tags: Urinary Infections, Homeopathic Remedies for Urinary Infections, Homeopathic Medicine for Urinary Infections, Homeopathic Treatment for Urinary Infections, Urinary Infections in Male, Urinary Infections in Female, Urinary Infections in women, Urinary Infections in men.