EFFECT OF HOMOEOPATHIC MEDICINES IN CASES OF RENAL FAILURE
Abstract: Renal failure is a challenge for the modern medical world and with the changes towards a cosmopolitan lifestyle; its incidence is increasing manifold. Patient is often left with practical interventional treatment. Renal replacement therapies may prolong life, but the quality of life is severely compromised. In 2015, according to projection by World Health Organization (WHO) and the Latin American Society of Nephrology and Hypertension (SLANH), there is growing trend due to the exacerbation of lifestyles with few healthy one. Classical homoeopathy may be considered a potential therapeutic modality in severe pathologies. Further studies are required to help patient with classical homoeopathy regarding severe procedure such as dialysis which also causes physical and economic problems.
Keywords – acute kidney disease, chronic kidney disease, RIFLE criteria, polycystic kidney, renal dropsy, azotemia, glomerulonephritis.
ABBREVATIONS – acute kidney disease (AKD), chronic kidney disease (CKD), World Health Organization (WHO), end-stage renal disease (ESRD), Latin American Society of Nephrology and Hypertension (SLANH), risk, injury, failure, loss, and end-stage disease (RIFLE), systemic lupus erythematous (SLE), glomerular filtration rate (GFR), computed tomography (CT).
METHODOLOGY- The data related to this article is collected from the source books like Practice of Medicine by Archith Boloor and Ramadas Nayak, Practice of Medicine by Kamal Kansal and Rakesh Kaushal, Homoeopathic Materia Medica by J.T.Kent , William Boericke, John Henry Clarke.
INTRODUCTION- Renal failure is characterised with loss of function resulting in the accumulation of metabolites in blood. As a result, the balance of fluids and electrolyte in the body gets disturbed, thereby causing serious health trouble. (1)
TYPES: 1- Acute kidney disease (AKD)
2- Chronic kidney disease (CKD)
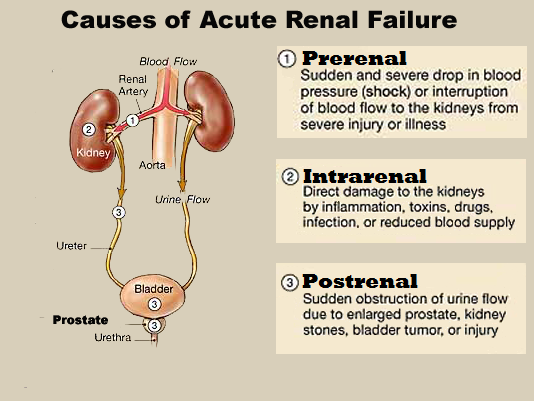
Acute kidney disease (AKD) – AKD is defined as sudden deterioration of kidney function, which is usually but not invariably, reversible over a period of days or rarely over few weeks. AKD was previously known as acute kidney failure, the other term used for this is azotaemia. There is a sudden increase in metabolic waste products (urea and creatinine) in the blood with consequent development of uraemia. (2, 5)
CAUSES:
- Renal artery obstruction, glomerulonephritis
- Kidney stones
- Prostate cancer, cervical cancer
- Heart attack, blood or fluid loss
- Liver failure
- Lupus(2)
SYMPTOMS –
- Decrease urine
output
- Fits and coma in severe cases
- Dyspnoea due to fluid over dose
- Epistaxis, gastrointestinal bleed
- Oedema of legs and feet
- Crepitation(2)
RIFLE criteria – It indicates an increasing degree of renal damage, also help in distinction between AKD and CKD. It has three stages: (2)
| Risk (stage 1)-. | Increased serum creatinine into 1.5 times within 48 hours | Urine output <0.5ml/kg/hour into 6 hours |
| Injury (stage 2)- | Increased serum creatinine into 2 to 3 times. | Urine output <0,5 ml/kg/hour into 12 hours |
| Failure (stage 3) | Increased serum creatinine into 3 times | Urine output, 0.3 ml/kg/hour into 24 hours or anuria for 12 hours |
| Loss | Persistent AKD = Complete loss of renal function (4 weeks) | |
| End stage of kidney disease | Persistent renal failure >3months |
GFR criteria Urine output
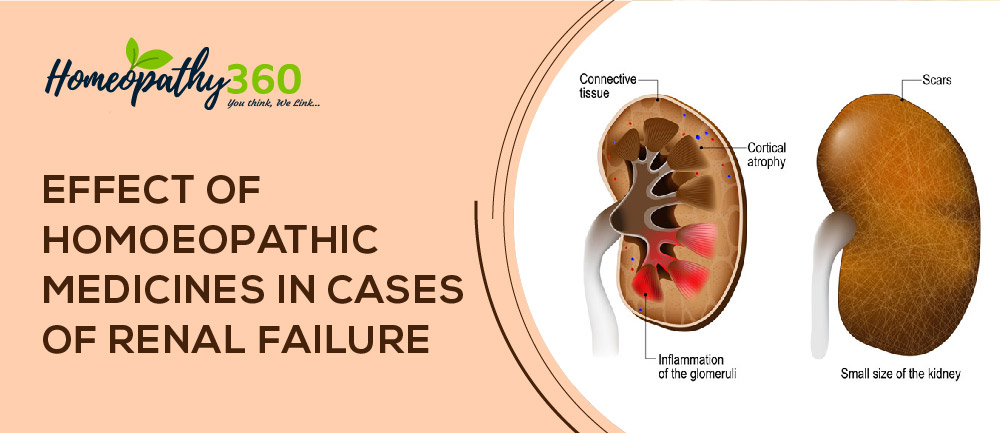
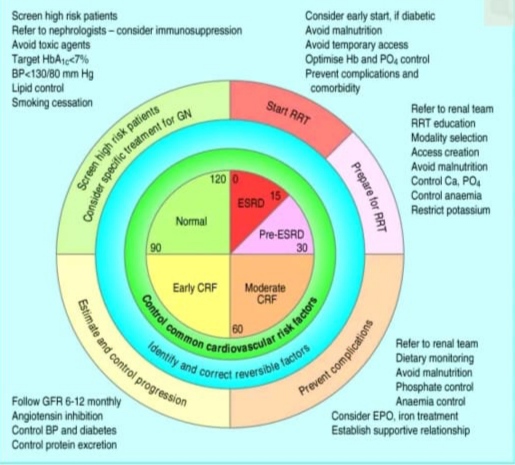
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE (CKD)- It was previously termed CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE or INSUFFICIENCY. It refers spectrum of long standing (more than 3 months) usually progressive process associated with irreversible changes in renal function and decline glomerular filtration rate (GFR).(2)
Chronic kidney disease is now recognised as a major medical problem worldwide. The global burden of disease study 2015 ranked chronic kidney disease as 17th among the causes of death globally.(3)
CAUSES –
- Renal stones
- Glomerulonephritis
- Prostate enlargement
- Alport syndrome
- Polycystic kidney
- Amyloidosis, SLE
- Diabetes(2,4)
SYMPTOMS –
- Polyuria, nocturnal
- Nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite
- Fatigue, weakness
- Oedema of legs and pleural effusion
- Hypertension(2)
INVESTIGATION-
- Serum creatinine
will be elevated
- Serum urea will be elevated
- Urine analysis may show proteinuria, red cell casts
- Ultrasound will show shrunken kidneys in CKD
- Chest radiograph may show pulmonary oedema and pleural effusion
- Plain abdomen radiography and CT scan to exclude low density renal stones
- ESR will be raised(2)
COMPLICATION –
- Hyperkalaemia,
hypocalcaemia
- Pericardial effusion, pericarditis
- Encephalopathy
- Urinary tract infection, septicaemia, pneumonia
- Anaemia, increased blood loss
- Toxic effects due to uraemia(2,4)
MANAGEMENT –
- Restrict
dietary protein
- Restrict salt intake
- Vitamins should be taken
- Potassium balance should be maintained
- Dialysis in severe cases(2)
Homoeopathic management –
- Apocyanum cannabinum – Renal dropsy, turbid, hot urine, Burning in urethra after urinating. Urine scanty but flows easily. Dropsy with thirst. <cold >in hot weather. (7)
- Apis mellifica – Burning and soreness when urinating, Dropsy with thirstlessness. Scanty high coloured urine, incontinence. Last drop burns and smarts < heat, touch > cold, open air.(6)
- Benzoicum acidum – Highly coloured urine, Strong smelling, soreness and burning in kidney region, sheets stains brown urine, Renal Insufficiency.(6)
- Berberis vulgaris – Burning pain, sensation as if some urine remained after urination, bubbling sensation. Pain in thigs and loins on urinating, Inflammation of kidneys < stooping, sitting >standing, Urine thick, yellowish like whey, Renal stones (6)
- Cantharis vesicatoria– Intolerable urging and tenesmus, bloody urine, cutting and burning in renal region. Urine scalds as if passed drop by drop. Constant desire to urinate, Hematuria, Inflammation of kidneys. (6)
- Ampelopsis quinquefolia – Renal dropsy, rumbling in the abdomen, high level of creatinine, vomiting, purging, cold sweat, and collapse are leading symptoms. (6,7)
- Arsenicum album – Urine scanty, burning when urinating Albuminuria, felling of weakness in abdomen after urination, retention of urine, high level of serum creatinine in blood. (6,7)
- Lycopodium clavatum – Severe pain before urinating, incontinence of urine, renal calculus, urine flows in feeble stream, red sand in urine can be seen, Patient has to wait for long time for passing urine <4 pm -8 pm. (6,7,10)
- Helleborus niger – Scanty urine with sediment like coffee ground, feeble stream, deep coloured urine. Dropsy, convulsions, bladder distended, serum creatinine highly increased. <evening until morning, uncovering. (6,7)
- Urea pura – Tearing pain from bladder to groin, standing, albuminuria, bloody urine, general dropsy, oedema of pudenda. Urine brown in colour, uraemia. (6,7)
- Cuprum arsenicosum– Uraemic convulsions, kidney action deficient, renal inefficiency and uraemia. Garlic like odour in urine with high specific gravity, increased acetones and di-acetic acid.(9)
- Mercurius corrosivus – Intense burning in urethra, urine hot, burning, scanty, suppressed, bloody greenish discharge, aluminous, tenesmus of bladder. Stabbing pain extending up urethra in bladder, preparation after urination. (10)
- Terebinthiniae oleum – Strangury with bloody urine, scanty, suppressed, odour of violet, urethritis. Inflamed kidneys, pressure in kidney when sitting going off during motion. Haematuria, spasmodic tenesmus of bladder. (6,7)
- Serum anguillae – Whenever kidney become acutely affected from cold, infection, oliguria, anuria, albuminuria, arterial hypertension without oedema. It is a renal remedy, haematuria, difficult urine secretions. (7)
- Petroselinum sativum– Abluminous, yellow discharge from urethra, creeping and crawling throughout whole length of urethra. Burning and tingling from perineum through urethra during urination, pain in urination cause him to shiver, dance around the room in agony. (7)
- Pareira brava – Excruciating pain in lumbar region, dropsical swelling of feet and legs, discharge of mucus from urethra, urine smell strongly of ammonia contains thick with mucus, dribbling of urination after micturition. Can only emit urine when he goes on his knees pressing head firmly against the floor, dysuria. (7)
- Cicuta virosa – Frequent urination, urine propelled with great force, retention of urine. Convulsions with violent distortion of the body.(7)
| CONDITIONS | HOMOEOPATHIC MEDICINES |
| Inactivity of kidney | Benzoicum acidum, Helonias dioica, Kalium nitricum, Solidago virgaurea, Terebinthiniae oleum |
| Weakness in kidneys | Apis mellifica, Arsenicum album, Benzoicum acidum, Berberis vulgaris, Helonias dioica, Solidago virgaurea |
| Function of kidney deranged | Apis mellifica, Digitalis purpurea, Solidago virgaurea |
| Kidneys Inactive | Aconitum napellus, Apis mellifica, Serum anguillae, Stramonium, Terebinthiniae oleum |
| Kidneys inactive in children | Aconitum napellus, Apis mellifica, Stramonium |
| Torpid action of kidneys | Apocyanum cynapium |
| Scanty and smoky urine | Terebinthiniae oleum |
| Kidney inflamed with heart failure | Adonis vernalis, Arsenicum album, Digitalis purpurea, Glonoinum, Strophanthus hispidus, Veratrum viride |
| Kidney inflammed with uraemic symptoms | Ammonium carbonicum, Arsenicum album, Belladonna, Cannabis Indica, Carbolicum acidum, Cicuta virosa, Cuprum arsenicosum, Helonias dioica, Hyoscyamus niger, Opium, Stramonium, Urea |
| Uraemia | Ammonium carbonicum, Belladonna, Carbolicum acidum, Cuprum arsenicosum, Helonias dioica, Mercurius corrosivus, Opium, Veratrum viride(2) |
CONCLUSION –There is no specific remedy in any disease in homoeopathy. The specific remedy to the case is the remedy selected on the basis of totality of the symptoms. At all levels, in early stage of disease, when prognosis is favourable, and in terminal cases, when prognosis is unfavourable, the disease effects and suffering should be palliated by an acute remedy selected on acute totality of the particular case. The state of patient with end stage renal failure or progressive reversible chronic renal disease is very pathetic not only for the patient itself, but also for the family and the society as a whole. In homoeopathic treatment, case individualisation, modalities, and mental symptoms are the necessary part to select find out the exact simillimum homoeopathic medicine. Homoeopathy helps to prevent a large number of cases progressing to haemodialysis and renal transplant.
REFRENCES-
- Qiu Z, Zheng K,“Prescription of physical exercise in a patient with kidney failure”. NCBI,2017 Feb 2020.
- Boolor A. Exam preparatory Manual for Undergraduates, New Delhi: Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers(P)Ltd;2017.
- Jha V, Modi G. Uncovering the rising kidney deaths in India. The Lancet. 2017 ;5(1): 14-15.
- Thomas R, Sedor JR. Chronic Kidney disease and its complications. NCBI .2008 ;35(2).
- Mohan H. Textbook of Pathology, New Delhi: Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers(P)Ltd; 2010.
- Clarke JH. A Dictionary of practical Materia Medica, New Delhi: B.Jain Publishers(P)Ltd;2014.
- Boericke W. New Manual Of Homoeopathic Materia Medica With Repertory, New Delhi: Indian Books And Publishers;2013.
- Boolor A. Exam preparatory Manual for Undergraduates, New Delhi: Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers(P)Ltd;2017.
- Kansal K, Kaushal R. Textbook Of Practice Of Medicine With Homoeopathic Therapuetics, New Delhi: B.Jain Publishers(P)Ltd;2017.
- Kent JT.Lectures On Homoeopathic Materia Medica, New Delhi: B.Jain Publishers(P)Ltd;2013.
About Author:
Dr Anit Acharya
Assistant professor
Department of Materia Medica
Dr MPK Homoeopathic Medical College, Homoeopathy University,Jaipur
Dr Ayushi Malhotra
PG Scholar, Department of Materia Medica
Dr MPK Homoeopathic Medical College, Homoeopathy University, Jaipur
Dr Aishwarya Pratap Singh
PG Scholar, Department of Materia Medica
Dr MPK Homoeopathic Medical College, Homoeopathy University, Jaipur