ABSTRACT:
Introduction: Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a disease in which there is an abnormal amount of androgen production in the body along with multiple cysts in the ovaries. The prevalence rate is approximately 6% (according to National Institute of Health Consensus 1990) to 20% (according to Rotterdam 2003 ) in women of the reproductive age group. Aetiology: Excessive secretion of androgens is the main cause. Clinical features: Irregular menstrual periods, hirsutism, acne and obesity are the common clinical features. Treatment: Lifestyle management and medications like contraceptive pills and metformin are commonly used. However, in homoeopathy symptom similarity is the core basis of prescription, thus a lot of medicines are available for the treatment of this disease.
Keywords: Homoeopathic medicine, polycystic ovarian syndrome, hirsutism, high androgen level, infertility, anovulation, amenorrhoea.
Abbreviations: Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), American society for reproductive medicine (ASRM), European society of human reproduction and embryology (ESHRE), ultrasonography (USG), sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG), follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinising hormone (LH), insulin ratio (IR), dehydroepiandrosterone sulphate (DHEAS), Laparoscopic ovarian drilling (LOD)
INTRODUCTION:
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a condition in which the ovaries produce abnormal amounts of androgens, male sex hormones that are usually present in women in small amounts. The name polycystic ovary syndrome describes the numerous small cysts (fluid-filled sacs) that form in the ovaries. The prevalence rate is approximately 6% (according to National Institute of Health Consensus 1990) to 20% (according to Rotterdam 2003) in women of the reproductive age group.1
AETIOLOGY: 2, 3
- This disorder is characterised by excessive production of androgens by ovaries and from and renal glands. Abnormal regulation of the androgen forming enzyme i.e., P450 C17, is one of the main causes of its excess production from these glands.
- Dysregulation of CYP 11a gene
- Apart from dysregulation of P450 C17 enzyme, adrenals are also stimulated to produce excessive androgens by stress and high prolactin levels.
- Hyperinsulinaemia leads to increased production of androgens, by stimulation of theca cells.
- Obesity(central) is an important contributory factor for the development of PCOS.
- Higher prevalence has been associated in first-degree relatives with PCOS.
- Congenital virilising disorders,
- Above-average or low birth weight for gestational age.
- Premature adrenarche, use of valproic acid as an antiepileptic drug. Studies have also suggested that there is a higher prevalence in Mexican-Americans than non-Hispanic whites and African Americans.
CLINICAL FEATURES:3, 4
The most common sign and symptoms of PCOS include:
- Irregular periods: Abnormal menstruation involves scanty or missing periods, or not having a period at all. It may also involve heavy bleeding during periods.
- Hirsutism: Abnormal and excess facial hair and heavy hair growth on the arms, chest and abdomen in women.
- Acne: Acne, especially on the back, chest and face are commonly seen in PCOS. These may continue past the teenage years and may be difficult to treat.
- Obesity
- Acanthosis nigricans: Dark colouredpatches of dark skin, especially in the folds of your neck, armpits, groin (between the legs) and under the breasts.
- Skin tags: these are often found in the armpits or on the neck.
- Thinning hair
- Infertility: PCOS is the most common cause of female infertility. Decreased frequency or lack of ovulation can result in not being able to conceive.
DIAGNOSIS: 2
- Diagnosis is based upon the presence of any two of the following three criteria, as per the American society for reproductive medicine (ASRM) / European society of human reproduction and embryology(ESHRE), 2003:
- Oligo and/ or anovulation.
- Hyperandrogenism (clinical and/ or biochemical)
- Polycystic ovaries
- In USG:
- Ovaries are enlarged in volume (≥ 10 cm3)
- Increased number (>12 ) of peripherally arranged cysts (of 2-9 mm in diameter) is seen.
- Ovarian capsule is thickened and pearly white in colour.
- Serum values:
- LH levels is elevated and/ or the ratio LH:FSH is > 2:1.
- Raised fasting insulin levels >25 µIU/ml and fasting glucose to insulin ratio <4.5 suggests IR. Levels of serum insulin response > 300 µIU/ml at 2 hours post glucose (75 gm) load, suggests severe IR.
- Raised level of oestradiol and estrone- the estrone level is markedly elevated.
- SHBG level is reduced.
- Hyperandrogenism- androstenedione is raised.
- Raised serum testosterone (> 150 ng/dl) and DHEAS may be marginally elevated.
TREATMENT:5
- Lifestyle changes:
- You can lose weight by exercising regularly and eating a healthy, balanced diet.
- Weight loss of just 5% can lead to a significant improvement in PCOS.
- Your diet should include plenty of fruit and vegetables, (at least 5 portions a day), whole foods (such as wholemeal bread, wholegrain cereals and brown rice), lean meats, fish and chicken.
b) Medicinal treatment:
- Contraceptive pill may be recommended to induce regular periods, or periods may be induced using an intermittent course of progestogen tablets (which are usually given every 3 to 4 months, but can be given monthly).
- Clomifene is usually the first treatment recommended for women with PCOS who are trying to get pregnant. Clomifene encourages the monthly release of an egg from the ovaries (ovulation).
- Metformin is used to lower blood sugar levels in patients suffering from PCOS. It also stimulates ovulation and regulates monthly periods.
- Medicines to control excess hair loss and hirsutism are spironolactone, flutamide, etc.
- Orlistat – to decrease weight in over weight females
- Statins- helps to reduce blood cholesterol levels
- Acne treatments are also used.
- Laparoscopic ovarian drilling (LOD) can be used to treat fertility problems.
COMPLICATIONS:2,4
- Diabetes.
- High blood pressure.
- Cardiovascular disease.
- Endometrial hyperplasia.
- Endometrial cancer.
- Sleep disorders such as sleep apnoea.
- Depression and anxiety.
- Infertility
- Miscarriage
HOMOEOPATHIC TREATMENT:
After repertorisation of all the common symptoms of PCOS, the following medicines appeared, as shown in figure-1.6
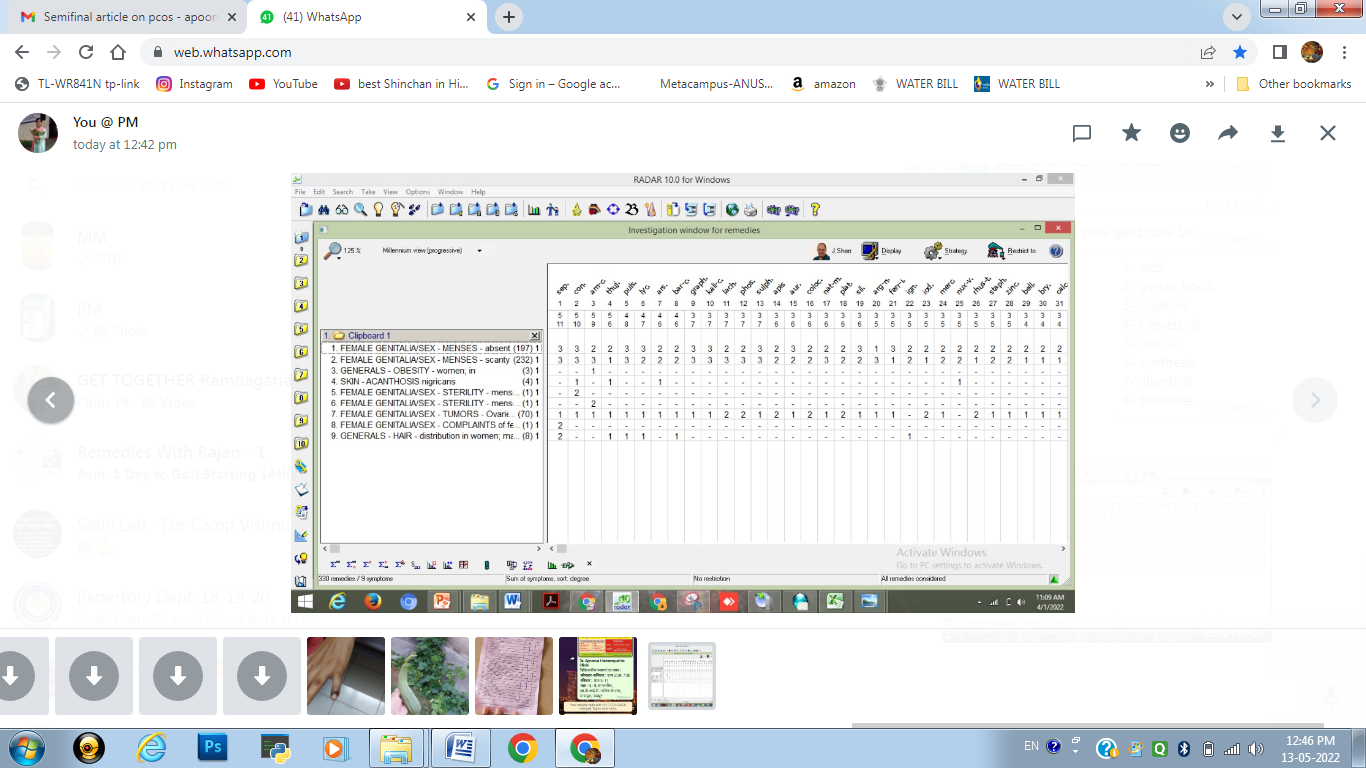
Figure -16
Symptoms of some important homoeopathic remedies:7,8
- Sepia officinalis:
Too early, too scanty and flow present only in morning with great weakness< morning, indoors and > in open air; menses are regular but scanty and dark and lasting for only one day.
Before menses : There is sadness and weeping; shuddering; foul odour and taste in mouth; tongue is very foul, but cleanses at each period, and returning again when flow ceases; burning, excoriation and smarting in vulva; sensation of distension at genitals.
During menses: Congestion and stinging pains in ovarian region, running around from the back over each hip, there is bearing down pain from uterus. Tenderness of female parts < touch. Painful stiffness, apparently in uterus; crampy colic with bearing down pains and sensation as if she must cross her legs to keep everything from coming out of vulva; constipation with sensation of a heavy lump in anus ; soreness of perinuem; foetid urine, deposition of clay coloured sediment, which adheres to bottom of vessel. Restlessness and sleeplessness; empty sensation at pit of stomach; drawing pain in abdomen and limbs; palpitation and dyspnoea; spasmodic colic and pressure over sexual organs along with headache, weakness of vision, nausea, hard stool and rigidity of limbs.
After menses: dryness of vulva and vagina, causing a disagreeable sensation when walking; offensive sweat in axilla and soles; flooding during climaxis or pregnancy, fifth and seventh month; there is much pain and weakness in small of back.
- Conium maculatum:
Menses are irregular too early and too feeble, or too late and too scanty, of brownish coloured blood. Dysmenorrhoea with pains extending to left chest; labour like abdominal pains, extending into thighs. Ovaritis; ovaries are enlarged and indurated; lancinating pains. Ill effects of repressed sexual desire or suppressed menses or from excessive indulgence. Breasts enlarge and become hard and painful before and during menses. Induration of cervix and os is present. Rash before menses. Itching around the pudenda. Unready conception (sterility) is present.
- Ammonium carbonicum:
Before menses: Face becomes pale. There is pain in abdomen and also small of back. No appetite. At commencement there are cholera like symptoms.
During menses: she is very sad and fatigued, especially in thighs with yawning, toothache, pain in small of back and chilliness. Menstrual flow increases at night, it is blackish, in clots, passing off with spasmodic pains in abdomen and hard stools. Menses are profuse and acrid, these make thighs sore and causes burning pain; too late, scanty and short, always accompanied by frontal headache; very nervous and restless; exhaustion with defective reaction; there is sleeplessness during menses; diarrhoea before and during menses; there is blood from rectum during menses.
- Thuja occidentalis:
A good medicine for Cysto- ovarium. There is inflammation with pain in left ovary. Pain extends through left iliac region into groin and sometimes into left leg. <from walking or riding, so she has to lie down (during menses); burning pain in ovary, ovarian affections are worse during menses. Menses are scanty and retarded.
- Pulsatilla pratensis:
There is amenorrhea. Menses are suppressed from wet feet, nervous debility or chlorosis. Tardy menses. Too late, scanty, thick, dark, clotted, changeable, and intermittent flow. There is chilliness, nausea with a downward pressure and pain. Diarrhoea during or after menses.
- Lycopodium clavatum:
Menses are too late; too long lasting and are too profuse. Vagina is dry. Burning and stinging pain in ovaries, > by urination. Sharp, shooting pains extending from right to left ovarian region. Dryness of vagina. Painful coition. Discharge of blood from genitals, during stool.
- Arsenicum album:
Ovaritis with burning, lancinating pains, as if hot coals were burning the part, accompanied by throbbing, >from hot application and much < by cold; restlessness, somewhat relieved by constantly moving the feet; burning pain in back while lying quietly on it; drawing, stitching pain starts from right ovary goes and into thigh.
- Baryta carbonica:
Menses are scanty and they last for only a day. Before menses there is toothache, colic and leucorrhoea. During menses there is a cutting and pinching type of pain in abdomen; bruised pain in small of back. This remedy is especially suitable to dwarfism women with scanty menses and troublesome weight about the pubis, in any direction.
REFERENCES:
1- National library of medicine. Metabolic Syndrome and PCOS: Pathogenesis and the Role of Metabolites [Internet]. 2021 Dec 14 [cited 2022 April 30]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8709086/
- Dutta DC, Konar H(ed.)Textbook of gynecology.2016.Jaypee brothers medical publishers (P) Ltd.
- Johns hopkins medicine. Polycystic ovary syndrome(PCOS)[Internet]. c2022 [cited 2022 May 4]. Available from: https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/polycystic-ovary-syndrome-pcos
- Cleveland clinic. Polycystic ovary syndrome(PCOS) [Internet]. c2022 [cited 2022 May4]. Available from: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/8316-polycystic-ovary-syndrome-pcos )
- NHS. Polycystic ovary syndrome[Internet]. [cited 2022 May 3] . Available from: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/polycystic-ovary-syndrome-pcos/treatment/
- Schroyens F.editor. Augmented clinical synthesis. Noida: B Jain publishers; 2016.
- Lilienthal S. Homoeopathic therapeutics. 24th ed. New delhi: B. Jain publishers (P) Ltd; 2016.
- Boericke W. Boericke’s new manual of homoeopathic materia medica with repertory. 3rd ed. Noida: B Jain Publishers;2019.
About Author:
Dr Ruchi Mehta
1-Associate/ Assistant Professor, Department of gynaecology and obstetrics, Dr MPK Homoeoepathic medical college, Saipura, Sanganer, Jaipur.
Dr Apoorva Saxena
2-MD, Department of Repertory, Dr MPK Homoeoepathic medical college, Saipura, Sanganer, Jaipur





