Prescription writing for a Homoeopathic Physician
ABSTRACT:
The medical prescription is a legal, written document assigned by a registered medical physician to the dispenser to dispense the selected medicine in the instructed dose, mode of intake for a particular patient at a particular time. The word “prescription” derives from “pre” before and “script” means written or writing, which denotes that it is an order or a health care program implemented by a physician in the form of instructions which govern the plan of care for an individual patient. Errors in prescription writing can occur mainly due to human errors. Some of the common errors observed during prescription writing can be attributed to the wrong format, hastily prescribing ,lack of clarity in comprehending the spelling which can lead to pharmacist misreading or misinterpreting the prescription, dispensing the wrong medicine or dosage and providing ambiguous information to the patient. According to World Health Organization(WHO) recommendations, prescriptions should identify the professional, the patient, the mode of administrations, as well as the medicine’s pharmaceutical form, dosage, frequency of use, duration of treatment long with patient guidance and information. It’s the responsibility of a physician to give full attention as it can lead to serious repercussions resulting in undesirable consequences such as worsening of treatment, increased cost of treatment and other serious adverse effects.
KEYWORDS: prescription, dispensing, pharmacist, doctor, patient, error, medicine, dose.
INTRODUCTION:
As a kid when I was taken to a doctor’s clinic I was always fascinated with the doctor’s stethoscope, torch, revolving chair as I enter the chamber but one thing which always seems alien to me was a Doctor’s prescription. There are countless meme and jokes on a doctor’s handwriting as for a layman its difficult to decode a doctor’s handwriting. Back in time I wondered how the poor pharmacists can make heads or tails of the instructions. But once I entered in the medical school , the first year pharmacy class comes the chapter “PRESCRIPTION WRITING”.
Where it’s taught that for a physician prescription Is the most important tool for treating it’s patient. It’s the basis of any therapeutic transaction between a physician and patient. The word prescription is derived from two latin words, “Para” meaning ‘before’ and “scribo” meaning , ‘I write’ (‘praescripto’). Prescription is a written document by a physician to the dispenser for dispensing the medicine, and also to the patient for the intake of the medicine. Thus prescription order is a part of the professional relationship between prescriber, pharmacist and the patient. The physician may choose to dispense the medication himself, where he needs to record the details of the prescription in his case record. But when the directions are given to the dispenser, it becomes a valuable document and must be properly written and preserved by the pharmacist, compounder or the patient after it has been served, thus also caries legal implications.
Since antiquity the evidence of prescription writing were found in the ancient Egyptian writings. These includes Kahun papyrus of 2000 B.C. which are medical prescriptions written in hieratic Egyptians writing.
The Prescription symbol (Rx) currently in use links pharmacy today to ancient mythology, and which appears on every prescription. The Rx has different interpretations. This symbol originated in medieval manuscripts as an abbreviation of the latin verb ‘recipere’, specifically the second person singular imperative for recipe meaning “take” thus “take thou”. In the past this was not have been a direction to the patient rather to the pharmacist, preceding the physician’s “recipe” for preparing a medication. The most popular interpretation is that it could have derived from the ancient Egyptian Eye symbol. The Eye of Horus (symbol of good and restored health). As William Osler wrote in 1910, “In a cursive form it is found in medieval translations of the works of Ptolemy the astrologer, as the sign of the planet Jupiter. As such it was placed upon horoscopes and upon formula containing drugs to be given to sick, so that drug is free from all the harmful properties under the influence of the lucky planet.
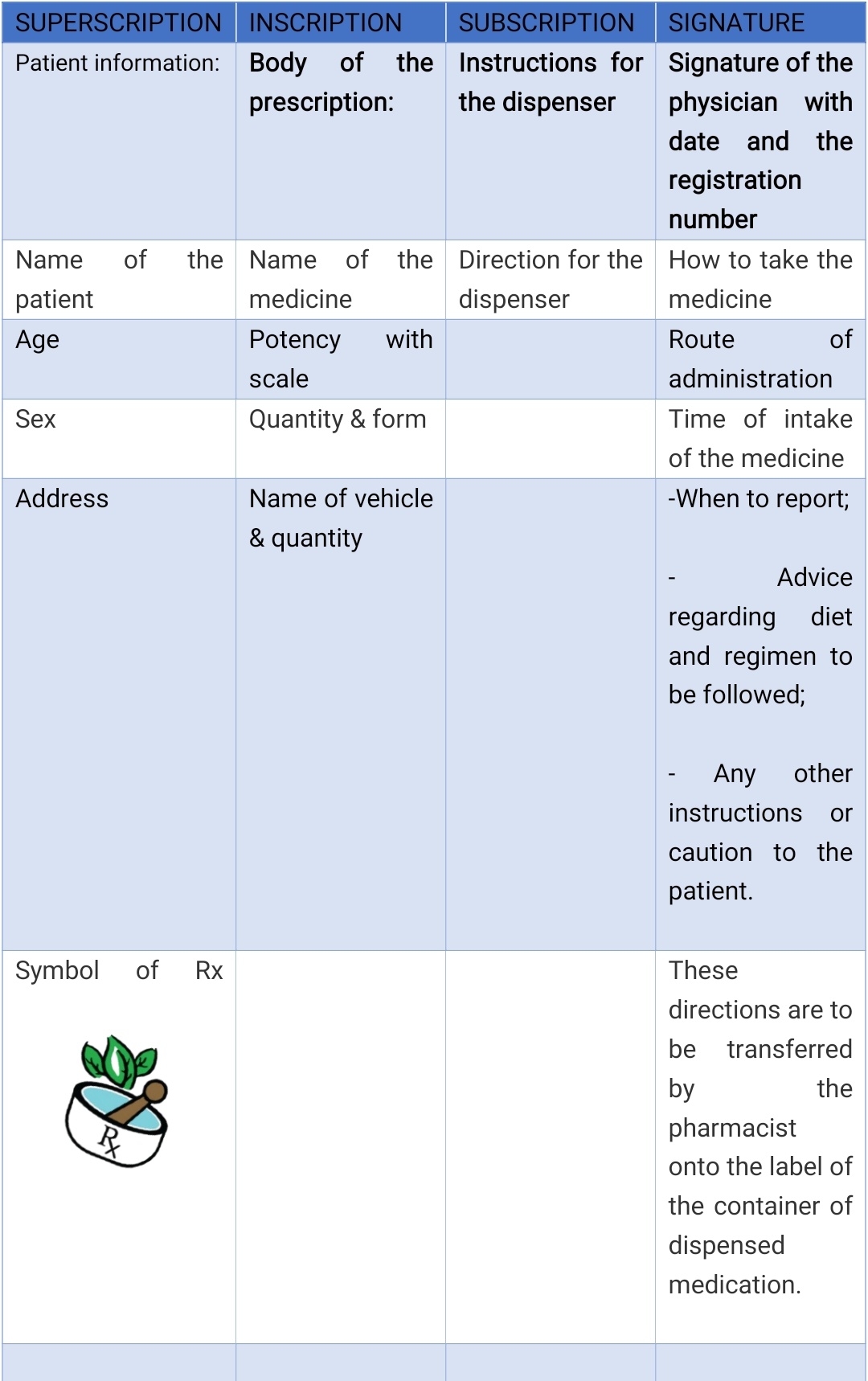
FORMS OR PARTS OF PRESCRIPTION:
A complete prescription mainly consists of 4 parts:
- SUPERSCRIPTION
- INSCRIPTION
- SUBSCRIPTION
- SIGNATURE
Prescriptions are dated at the time they are written and also when they are received and filled in the pharmacy. The ‘date’ helps the pharmacist to find out cases where prescription is brought for dispensing, a long time after it is issued. The date is important in establishing record of the patient.
PRESCRIPTION GUIDELINES FOR PHYSICIANS
* Prescriptions must always be written in a definite pattern, as detailed. Proper arrangement of the form of prescription is to be maintained for uniformity and standard, as it is universal.
* It should be legible and neatly written, so as to be easily interpreted.
* The information should be complete, accurate and unambiguous.
* The homoeopathic physician should avoid prescribing inimical homoeopathic medicines as also those medications that are not homoeopathic.
* Prescriptions may be written in simple form or in Latin.
In earlier time Latin was part of writing prescription orders as it was considered the international language of medicine. From there onwards Latin words, phrases and abbreviations were carry forward. In the present scenario routine prescriptions are written in English due to its simplicity and use of Latin is gradually diminished. On the contrary there are a number of Latin terms and phrases, abbreviations in the subscriptions which were used traditionally continue to find a place in prescription writing. The arguments for the continued use of Latin are
– Pharmacists in all countries understand it.
– Latin forms a healthy shorthand for the busy practitioner.
– It is argued that it is advisable, the patient should not learn the nature of remedies prescribed for him.
Hence the Latin names should be used for the directions to the dispenser. The dispenser must write the directions on the label either in English or in the local language. But, when in doubt, write in simple form.
GUIDELINES FOR A GOOD PRESCRIPTION AND PATIENT COMPLIANCE
In order to gain maximum benefit from the prescription, there has to be an effective communication amongst the prescriber, dispensing pharmacist and the patient. The instructions and directions for drug use, which prescribers indicate on prescription orders and which dispensing pharmacists transfer to prescription labels are important for effective cure. For effective patient compliance, the following guidelines may be followed.
Guidelines for Prescribers
* Name and strength of the dispensed medication should be recorded on the prescription label unless otherwise directed by the prescriber.
* Whenever possible, specific times of the day for drug administration should be indicated.
* Use of potentially confusing abbreviations should be discouraged.
* Vague instructions that are confusing to patient are to be avoided.
* Metric system of weights should be used.
Guidelines for the Dispensing Pharmacist
* When a prescription is presented for dispensing, it should be received by the pharmacist without any discussion or comment over it regarding the merits and demerits of its therapeutic efficiency. The pharmacist should not even show any expression of alarm or astonishment, as such things may cause anxiety in the patient.
* It is not within the privilege of a pharmacist to add, omit or substitute the composition and nature of the prescription without the consent of the prescribe
* Pharmacists should indicate the following information on the prescription label: name, address, telephone number of the pharmacy, name of prescriber, strength and quantity of the dispensed medication (unless otherwise directed by the physician), directions for use, prescription number, date on which the prescription is dispensed, full name of the patient or any other information as felt necessary.
* Instructions to patient regarding directions for use of medication should be concise, precise and easily understandable by the patient.
* Directions for storage of the dispensed medication should also be mentioned.
For an ideal prescription Details pertaining to DOCTORS
Doctor’s full name (printed on the letterhead)
Doctor’s details such as address, consultation timings, telephone/ contact numbers should printed on the letterhead.
Doctor’s Qualification should printed on the letterhead. This means ALL the degrees, especially the primary degree, namely, M.B.B.S./B.D. S./B.V.Sc./ B.H.M.S.
Doctor’s registration number and the registering authority should be printed on the letterhead.
Doctor’s full signature and date, both in blue indelible ink. This is required to verify the authenticity of prescription in order to prevent misuse.
Date of prescribing- Also a legal requirement
Rx superscription- Not a legal requirement but most often used as a matter of practice. It comes from the Latin “Take Thou”
Doctor’s rubber stamp containing his full name, qualifications, and Reg. No. below his signature- More so to add to the authenticity of Prescriptions
Details pertaining to PATIENT
Patient’s Full Name
Patient’s age, weight
Patient’s address and telephone number (including Mobile No.)
Patient’s Sex
Details pertaining to medicine
Name of the medicine
Strength or potency of the medicine
Dosage Form-
Dosage & dosing instructions
Total Quantity
Refill information- If the doctor wants the prescription to be filled/dispensed only once, he should clearly write that it “SHOULD NOT BE REFILLED” or “DO NOT DISPENSE MORE THAN ONCE” at the bottom of the prescription (or get it pre-printed on the prescription blank). If the doctor wants the prescription to be refilled, he should clearly write the number of times the prescription should be refilled. This is very important to deter patients from refilling (repurchasing) the same prescription again & again unless so directed by the doctor.
Some Important Points to Remember ( Do’s and Dont’s)
Letterheads/prescription blanks should be kept secure to avoid misuse.
Overwriting on a prescription should be avoided. In case of overwriting, doctor must initial each correction.
Prescription may be typed/computer generated, but it has to be signed and dated by Doctor in blue indelible ink.
It is illegal to allow nurses/assistants to write prescriptions/medication orders
Doctors should always encourage pharmacies to call them up on telephone in case of any problems/ discrepancies/doubts/queries in their prescription.
One should avoid having names of two or more doctors on the same prescription pad (even if it is a husband and wife team). More so if they belong to different specialties or systems of medicine.
It is unethical for a doctor to prescribe medicines for his own use other than the simplest OTC medicines. Self medication as a concept is to be discouraged.
A doctor should not use another doctor’s prescription pad, even with his consent. Conversely a doctor should not allow another other doctor to use his/her prescription pad
The doctor should not write s.o.s. against any medicine. It is not an accepted abbreviation. The doctor should use the correct abbreviation – p.r.n. (pro re nata) or the English equivalent – ‘as and when required’. In such cases, the minimum dose interval, the maximum daily dose and maximum duration and the maximum quantities to be dispensed, should be specified.
Avoid unnecessary use of units.
Doctors should doubly careful in writing the potency & quantity of the drug/s. It is advisable to write the quantity in words also so that patients/clients do not manipulate the numbers.
Write in bold “DO NOT DISPENSE MORE THAN ONCE”, in the in the middle or bottom of the prescription (bearing in mind that sometimes what is written at the bottom is cut off by the patient).
Always write the potency for single ingredient drugs even if no other potency is marketed. You never know, when a new potency (higher or lower) would be introduced in the market.
In case of combination products, it is always advisable to write the potencies of all the individual components in order to eliminate any misinterpretation at the pharmacy.
Alterations/overwriting in the prescription are best avoided, but if any are made, they should be clear and unambiguous. Doctors should make sure to add their initials against the altered items.
Doctors should refrain from prescribing medicines of other systems of medicine.
CONCLUSION
Writing a prescription is both a science and art. For a homoeopathic physician the work is half done after selecting a medicine on the basis of principle of Homoeopathy and teachings of master Hahnemann. The physician should keep in mind that there are many essential and also legal requirements that are mandated in a practioner’s prescription. Thus there are some very important points (as per the Drugs and Cosmetics Act and Rules) that a doctor must remember, while undertaking this routine yet most significant task. Any negligence in writing a prescription may lead to fatal consequences including health. The present article is an attempt to gain insight into thoughtful and deliberate way of prescribing to avoid any errors. The condition for error- free prescribing must be propagated. While writing prescriptions this should be ensured that it is the most appropriate and in the best interest of the sick. It is but obvious that right selection of medicine, correctly written prescription and well explained that it will be taken correctly by the patient. It’s the duty of the physician to take this thoughtfully as lack of attention can lead to adverse effects. Errors in prescription writing are the most common form of preventable errors and Thus are an important target area for improvement.
REFRENCES
Ajay et.al. IDEAL DRUG PRESCRIPTION WRITING ; WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES; Volume 8, Issue 3, 634-654.
Amy Beth Dukoff, D.M.D.Did You Know Where Rx Came From? http://www.endomail.com/articles/ad13rx.html
Art & Science of Homoeopathic pharmacy https://homeoresearch.blogspot.com/2010/09/homoeopathic-prescription.html?m=1
de. Vries TP, Henning RH, Hogerzeil HV,Fresle DA. Guide to good prescribing – A practical manual .Geneva; World Health Organization;1994.Action programme on essential drugs.
Medical prescription/Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia.mht.
Davis T. Prescription Writing and the PDR.htm, updated 8/30/2005.
Donnelley RR. Principles of Prescription Writing and Other Pharmacotherapeutic Considerations, VOL 9,China, June 9, 2008, pp.25-31
Mercy ships bringing hope and healing. An essential medicines dosing guide based on the WHO model formulary 2008-Prescription writing guidelines.
Proposed guidelines for prescription writing & handling for drugs having misuse or abuse potential, proposed by FDA, Goa at the stakeholders meeting held on 23rd September, 2009.
Good practice in prescribing medicines – guidance for doctors.mht, General Medical Council, September, 2008.
Fox A. Safer Prescribing, p1–23. Workbook-Section 1, Prescription writing.
Nazar H, Nazar M, Rothwell C, Portlock J, Chaytor A, Husband A. Teaching safe prescribing to medical students; Perspectives in the UK. Adv Med Educ Pract. 2015;6:279-95
Prescription Pad – An Ultimate Prescription Writing Software, E-Prescription, Indian Prescription.htm, 2009.
“What lurks in your medicine cabinet?” USA Weekend. 2002-12-01. http://www.usaweekend.com/02_ issues/021201/021201healthsmart.html.
Dr.M.K.Sahani,M.D., Principles and practice of homoeopathic pharmacy for students; prescription writing; chapter 21, first edition 2007,pp- 175-178
Debnath.S,History of pharmacy https://www.researchgate.net/publication/321331560, Nov 2017