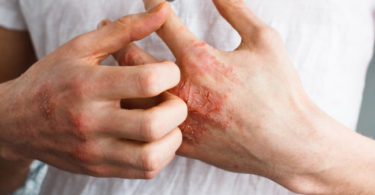
Damage to peripheral nervous system is called peripheral neuropathy. Peripheral neuropathies can impair sensory, motor or autonomic functions. It may be further divided as mononeuropathy (involving one one nerve) or polyneuropathy.
Causes of peripheral neuropathy:
A. Specific diseases:
1. Charcot Marie Tooth disease
2. Fabry Disease
3. Refsum Disease
4. Tangier Disease
5. Polyuria
6. Amyloidosis
7. Diabetes
8. Hypothyroidism
9. Sjogren’s Syndrome
10. Rheumatoid Arthritis
11. SLE
12. Scleroderma
13. Sarcoidosis
14. Celiac Disease
15. IBD
16. Uraemia,
17. Chronic Liver Disease
18. Leprosy
19. Lyme Disease
20. Guillain Barre syndrome
21. HIV
22. Herpes varicella zooster
23. Cytomegalovirus
24. Epstein Barr Virus
25. Hepatitis Viruses
26. Malignancy
B. Caused due to drugs:
Hydroxychloroquine, Amiodarone, colchicine, Disulfiram, Dapsone. Pyridoxine, isoniazid, phenytoin, Lithiun
C. Caused due to toxins:
Organophosphates, lead, Mercury, Thallium, Arsenic, Alcohol.
D. Nutritional deficiencies:
Vit B12( cobalamin), Vit B1, Thiamine Vit-B6 (pyridoxine), Vit E, pellagra, copper deficiency, gastric surgery.
E. Radiculopathies:
Due to joint degeneration, disk herniation leading to nerve compression like sciatica, carpel tunnel syndrome, cubital tunnel syndrome.
Symptoms:
• Numbness (loss of sensation)
• Formication, pins and needles sensations in hands and feet
• Burning sensation, Tingling, pricking sensation
• Altered sensation to touch
• Weakness
• Orthostatic hypotension
• Light headedness
• Heat intolerance
• Increased heart rate
Homoeopathic approach-
Homoeopathy works on holistic approach. It does not consider parts of body as separate but considers a person as a whole in both physical as well as mental aspect. It is most suitable approach for such diseases involving multiple systems.
Reportorial references
From Kent’s repertory:
Extremities, NUMBNESS: Arg-m., Arg-n., arn., ars-h., ars. aur, carb-ac., carb-an., carb-o., Carb-s., Carb-v., caust. fago., fl-ac., Gels., Graph., hyos., hyper., iod., kali-ar., kali-c., kali-p, led., Lyc., merc., mez., naja., nat-m., Op., Ox ac petr., phos.,plb., psor., puls., rhod., Rhus-t., Sec., sep., sil., stram., sulph.
Extremities, NUMBNESS, motion, amel. : Am-c., anac., aur.
Extremities, NUMBNESS, Upper extremities, hand, radial nerve, distribution of : Ph-ac.
Extremities, NUMBNESS, Upper extremities, hand, ulnar side: Plb.
Extremities, NUMBNESS, Upper extremities, hand, after writing: Agar.
Extremities, NUMBNESS, sole of : Alum., alumn., ars., bry., cann-i., cham., chel., Cocc., cupr., eupi., fl-ac., laur., merc-sul., nat-c., nux-v., olnd., plb., puls., raph., sec., sep., sulph., syph., thuj., zinc
Extremities, TINGLING, prickling, asleep: arn., ars., atro., bell., camph., carb-an., carb-o., carb-s., carb-v., con., cupr., gels., Graph., ign., kali-bi., kali-c., kreos., lach., led., Lyc., merc., morph., nat-m., op., ox-ac., Petr., ph-ac., Phos., plb., psor., Puls., rhod., Rhus-t., sec., sep., sil., stram., stry., sulph, verat., zinc.
Extremities, TINGLING, Upper extremities, hands, finger, tips : Acon-c., acon-f., acon., Am-m., cact., cann-s., colch., croc., fl-ac., hep., Kali-c., lach., nat-m., nat-s., rhod., rhus-t., sec., sep., sulph., thuj.
Extremities, FORMICATION : Acon., agar., alum., arg-n., ars-h., ars., bar-c., cact., camph., caps., carb-ac., carb-s., carl., caust., crot-c., hep., hipp., hydr-ac., ign., kali-ar., kali-c., lach., laur., Lyc., mez., nux-v., Ph-ac., phos., plb., psor., puls., rhod., Rhus-t., sabad., Sec., stram., stry., Tarent., teucr., verat., zinc.
Extremities, pain, burning : Abrot., anac., ars., bell., cann-i., carb-an., carb-v., chin., cocc., coloc., kali-ar., kali-br., kali-c., kali-p., kreos., laur., led., nit-ac., ph-ac., phos., plan., plat., plb., staph., vip.
Some of the important remedies:
Oxalic acid: Numb, weak, tingling. Pains start from spine and extend through extremities. Drawing and lancinating pains shooting down extremities. Backache; numb, weak, Myelitis. Muscular prostration. Wrist painful, as if sprained (Ulmus). Lower extremities blue, cold, insensible. Sensation of numbness. Multiple cerebral and posterior spinal sclerosis. Lancinating pains in various parts; jerking pains.
Picric acid: Causes degeneration of the spinal cord, with paralysis.Acts upon the generative organs probably through the lumbar centers of the spinal cord; prostration, weakness and pain of back, pins and needle sensation in extremities. Neurasthenia. Muscular debility. Heavy tired feeling. Myelitis with spasms and prostration. Writer’s palsy. Progressive, pernicious anaemia. Uraemia with complete anuria. Burning along spine. Great weakness. Tired, heavy feeling all over body, especially limbs; worse, exertion. Feet cold. Cannot get warm. Acute descending paralysis.
Graphites: Spinal pains. Pain in small of back with great weakness. Excoriation between thighs. Left hand numb; arms feel asleep;
Rhus tox: Limbs stiff paralyzed. The cold fresh air is not tolerated; it makes the skin painful. Pain along ulnar nerve. Tearing down thighs. Sciatica; worse, cold, damp weather, at night. Numbness and formication, after overwork and exposure. Paralysis; trembling after exertion. Tenderness about knee-joint. Loss of power in forearm and fingers; crawling sensation in the tips of fingers. Tingling in feet.
Sulphur: Burning in soles and hands at night. Numb fingers heaviness paretic feeling in limbs soles burn wants them uncovered,burning sensation with rush of heat.
Gelsemium: Centers its action upon the nervous system, causing various degrees of motor paralysis. General prostration. Dizziness, drowsiness, dullness, and trembling. Slow pulse, tired feeling, mental apathy. Paralysis of various groups of muscles about the eyes, throat, chest, larynx, sphincter, extremities, etc. Post-diphtheritic paralysis. Muscular weakness.
Phosphorus: Ascending sensory and motor paralysis from ends of fingers and toes. Burning of feet. Weakness and trembling, from every exertion. Can scarcely hold anything with his hands. Arms and hands become numb. Can lie only on right side. Post-diphtheritic paralysis, with formication of hands and feet.
Lycopodium: Numbness, also drawing and tearing in limbs, especially while at rest or at night. Heaviness of arms. One foot hot, the other cold. Profuse sweat of the feet. Pain in heel on treading as from a pebble. Painful callosities on soles; toes and fingers contracted. Sciatica, worse right side. Cannot lie on painful side. Hands and feet numb. Right foot hot, left cold. Cramps in calves and toes at night in bed. Limbs go to sleep. Twitching and jerking.
Kali phos: Neurathenia, paralytic weakness, progressive muscular atrophy, creeping sensation and intense pain along spine, prickling in hands and feet, numb fingertips, foot feels frost bitten, pain in soles, feet fidgety, subnormal temperature.
Causticum: Left-sided sciatica, with numbness. Paralysis of single parts. Dull, tearing pain in hands and arms. Heaviness and weakness. Numbness; loss of sensation in hands. better by warmth, especially heat of bed. Burning in joints. Restless legs at night.
Hypericum: Pain in toes and fingers, especially in tips. Crawling in hand and feet. Lancinating pain in upper and lower limbs. Neuritis, with tingling, burning pain, numbness and flossy skin
Arsenicum album: Sciatica. Burning pains. Peripheral neuritis. Diabetic gangrene. Ulcers on heel Paralysis of lower limbs with atrophy. Tingling in fingers, feet weak weary numb. Wooden feeling in soles, sore pain in ball of toes while walking, limbs heavy, restless feet. Sciatica amel. Walking and hot applications.
References:
Harrison’s principles of internal medicine
Kent’s repertory of homoeopathic material medica
Materia medica by William Boericke.