 Abstract
Abstract
The article explains aboutGangrene and its associated amputations which is aclinically challenging condition, but Homeopathy offers therapy options. The case presented herein, details about how the Homeopathic treatment helped in the prevention of amputation of a body part. Homeopathy stimulates the body’s ability to heal through its immune mechanisms; consequently, it achieves wound healing and establishes circulation to the gangrenous part. Instead of focusing on the local phenomena of gangrene pathology, treatment focuses on the general indications of the immune system, stressing the important role of the immune system as a whole. The aim was to show, through case reports, that Homeopathic therapy can treat gangrene thus preventing amputation ofthe gangrenous part, and hence has a strong substitution for consideration in treating gangrene.
Keywords: Gangrene, Homeopathy, Immune system
Introduction
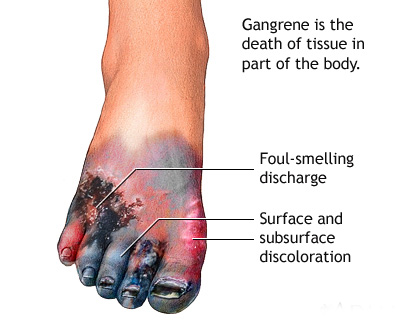
Gangrene is a type of necrosis caused by critically insufficient blood supply. This potentially life-threatening condition may occur after an injury or infection, or in people suffering from any chronic health problem affecting blood circulation.
Early stages of wet gangrene may include signs of infection, aching pain with swelling, a reddish skin color or blanched appearance if the area is raised above the level of the heart, coolness on the skin surface, ulceration, and a crackly sensation when the skin is pressed due to gas in the tissue.
Gangrenetypes
- Dry gangrene: More common in people with blood vessel diseases, diabetes, and autoimmune diseases, dry gangrene usually affects the hands and feet. It develops when blood flow to the affected area is impaired, usually as a result of poor circulation. In this type, the tissue dries up and may be brown to purplish-blue to black in color and often falls off. Unlike other types of gangrene, infection is typically not present in dry gangrene. However, dry gangrene can lead to wet gangrene if it becomes infected.
Wet gangrene: Unlike dry gangrene, wet gangrene almost always involves an infection. Injury from burns or trauma where a body part is crushed or squeezed can rapidly cut off blood supply to the affected area, causing tissue death and increased risk of infection. The tissue swells and blistersand is called “wet” because of pus. Infection from wet gangrene can spread quickly throughout the body, making wet gangrene a very serious and potentially life-threatening condition if not treated quickly. Types of wet gangrene include:
- Internal gangrene:If gangrene occurs inside the body due to blocked blood flow to an internal organ, then it is referred to as internal gangrene. This is usually related to an infected organ such as the appendix or colon.
- Gas gangrene:Gas gangrene is rare but dangerous. It occurs when infection develops deep inside the body, such as inside muscles or organs, usually as a result of trauma. The bacteria that causes gas gangrene, called clostridia, release dangerous toxins or poisons that wreak havoc throughout the body, along with gas which can be trapped within body tissue. As the condition progresses, the skin may become pale and grey, and make a crackling sound when pressed, due to the gas within the tissue. Gas gangrene warrants immediate medical treatment. Without treatment, death can occur within 48 hours.
- Fournier’s gangrene:Also a rare condition, Fournier’s gangrene is caused by an infection in the genital area. Men are affected more often than women. If the infection gets into the bloodstream, a condition called sepsis, it can be life-threatening.
Causes of gangrene
- Bloodplays a very important role in your health. Not only does it transport oxygen and nutrients throughout your body to feed cells, it delivers disease-fighting antibodies that protect your body from infection. When blood cannot travel freely throughout the body, your cells cannot survive, infection can develop, and tissue can die from gangrene. Any condition that affects blood flow increases your risk of gangrene, including:
- Vascular – Gangrene is seen invascular diseases such as peripheral arteriosclerosis, thrombosis of the large arteries, thrombosis of terminal aorta, etc.
- Infection– Gangrene is mainly produced by Clostridium perfringens, and other clostridia, bacteria such as streptococcal, staphylococcal may also produce certain forms of gangrene.
- Neoplasm– Multiple myelomas are generally associated with Raynaud phenomenon which produces gangrene.
- Neurological – Peripheral neuropathy, syringomyelia,transverse myelitis, may be associated with gangrene.
- Intoxication– One should keep in mind that use of ergot alkaloids may also be associated with gangrene.
- Trauma – Laceration of major artery of extremities or pressure from splinters may cause gangrene.
- Decreased temperature– Extremes of cold may produce frostbite which can ultimately lead to gangrene.
- Autoimmune diseasessuch as lupus erythematosus, sclerederma and rheumatoid arthritis may be associated with Raynaud phenomenon and gangrene.
- Endocrine – Gangrene can be associated with diabetes.
Symptoms
You may notice the following symptoms at the site of the dry gangrene:
- Dry and shriveled skin that changes color from blue to black and eventually sloughs off
- Cold and numb skin
- Pain may or may not be present
Symptoms of wet gangrene may include:
- Swelling and pain at the site of infection,
- Change in skin color from red to brown to black,
- Blisters or sores that produce a bad-smelling discharge (pus),
- Fever and feeling unwell,
- A crackling noise that comes from the affected area when pressed.
Internal gangrene is usually painful in the area of the gangrene. For example, a person with gangrene of the appendix or colon would be expected to have severe abdominal pain in the vicinity of the gangrene.
Gangrene Warning: If infection from gangrene gets into the blood, you may develop sepsis and go into septic shock. This can be life-threatening if not treated immediately. Symptoms of sepsis may include:
- Low blood pressure
- Rapid heartbeat
- Shortness of breath
- Change in body temperature
- Light-headedness
- Body pain and rash
- Confusion
- Cold, clammy, and pale skin
If you think you or a loved one may have sepsis, go to the emergency room immediately.
Prevention of gangrene
Foot care
- Check your feet daily for problems such as numbness, discolourations, breaks in the skin, pain or swelling. Report problems to your physicianimmediately.
- Avoid walking barefoot outside and wearing shoes without socks.
- Don’t use chemical preparations for corns and callusesor ingrown toenails. Instead, contact a podiatrist (a healthcare professional who specialises in foot care).
- Wash your feet daily with warm water. Afterwards, make sure you dry your feet thoroughly, particularly between the toes.
Wear shoes that fit properly and don’t squeeze or rub. Ill-fitting shoes can cause corns and callouses, ulcers and nail problems.
Smoking: Smoking can cause your arteries to become blocked, resulting in a loss of blood supply to your arms or legs.
Diet: Eating an unhealthy diet high in fat will make any existing atherosclerosis worse and increase your risk of developing gangrene.There are two types of fat – saturated and unsaturated. Avoid foods that contain saturated fats because they increase levels of “bad cholesterol” in your blood.
Foods high in saturated fat include:
- Meat pies
- Sausages and fatty cuts of meat
- Butter
- Ghee (a type of butter often used in Indian cooking)
- Lard
- Cream
- Hard cheese
- Cakes and biscuits
- Food containing coconut or palm oil
Alcohol: Drinking excessive amounts of alcohol will cause your blood pressure to rise, and also raise the level of cholesterol in your blood.
Exercise: A healthy, well-balanced diet and regular exercise will keep your blood pressure and cholesterol levels at a healthy level, helping prevent your blood vessels becoming damaged.
Moderate intensity physical activity is any activity that increases your heart and breathing rate. It may make you sweat but you’ll still be able to hold a normal conversation. Examples include:
Gangrene is a condition that occurs when body tissue dies. It is caused by a loss of blood supply due to an underlying illness, injury, and/or infection. Fingers, toes, and limbs are most often affected, but gangrene can also occur inside the body, damaging organs and muscles. There are different types of gangrene and all require immediate medical attention.
Homeopathictreatment
- Arsenicum album– Medicine for senile gangrene;gangrene accompanied by foetid diarrhoea; ulcers extremely painful with elevated edges, better by warmth and aggravation from cold; great weakness and emaciation.
- Bromium – Hospital gangrene; cancerous ulcers on face; stony hard swelling of glands of lower jaw and throat.
- Carbo vegetabilis – Senile and humid gangrene in the persons who are cachectic in appearance; great exhaustion of vital powers; marked prostration; foul smell of secretions; indolent ulcers, burning pain; tendency to gangrene of the margins; varicose ulcers.
- Bothrops– Gangrene; swollen, livid, cold with hemorrhagic infiltration; malignant erysipelas.
- Echinacea– Enlarged lymphatics; old tibial ulcers; gangrene; recurrent boils; carbuncles.
- Lachesis– Gangrenous ulcers; gangrene after injury; bluish or black looking blisters; vesicles appearing here and there, violent itching and burning; swelling and inflammation of the parts; itching pain and painful spots appearing after rubbing.
- Crotalus Horridus– Gangrene, skin separated from muscles by a foetid fluid; traumatic gangrene; old scars open again.
- Secale cornatum– Pustules on the arms and legs, with tendency to gangrene; in cachectic, scrawny females with rough skin; skin shriveled, numb; mottled dusky-blue tinge; blue color of skin; dry gangrene, developing slowly; varicose ulcers; boils, small, painful with green contents; skin feels too cold to touch yet covering is not tolerated. Great aversion to heat;formication under skin.
- Anthracinum– Gangrene; cellular tissues swollen and oedematous; gangrenous parotitis; septicemia; ulceration, and sloughing and intolerable burning.
- Cantharis – Tendency to gangrene; vesicular eruptions; burns, scalds, with burning and itching; erysipelas, vesicular type, with marked restlessness.
- Mercurius– Gangrene of the lips, cheeks and gums; inflammation and swelling of the glands of neck; pains aggravated by hot or cold applications.
- Sulphuric acid– Traumatic gangrene; haemorrhages from wounds; dark pustules; blue spots like suggillations; bedsores.
- Phosphoric acid– Medicine for senile gangrene. Gunpowder, calendula are also best medicines.
Discussion:
Dr Prabhakar Shetty (2012) explains that Homeopathy can bring blood supply to the limbs without By-Pass Surgery. Well simple Homeopathic medicine not only saves the foot and leg but the human life.Seema Maheshetal.(2015)studied that the Homeopathic therapy can treat gangrene without amputing the gangrenous part, and hence has a strong substitution for consideration in treating gangrene.Krishna Murthy et al.(2017)showed that diabetic footgangrene that was treated with homeopathic therapy avoided a need for amputation of the limb. From this case report, we would like to suggest that there are better options like homeopathic therapy for a patient with diabetic foot gangrene rather than considering them for the amputation.Dr Samarendra Kumar Mishra(2017)asked that the Pyrogen & Gunpowder with haphazard external application of Calendula-Q in dressing helped to save the life of the patient from beinghandicapped. In this case, a rarely used drug -Gun Powder played a major role in curing the patient and its high value needs to be well exposed scientifically in gangrene.Samarendra Prasad Mishra(2017)studied that septic gangrene of the foot in an elderly woman, whose prognosis was poor given that amputation of the leg below the knee had been advised. Full cure was effected by using the drugs Gunpowder and Pyrogen with topical dressings of Calendula-Q.
Conclusion:
Homeopathy is the best medicine for gangrene. It considers the totality of symptoms (even ones not obviously related to the pathology), along with the pathology itself. This makes for a holistic understanding of the patient’s immune status. With the right Homeopathic remedy, inflammation and wound healing process sets in and finally close up the wound. Within a short period, the remedy heals the gangrene, controls infection, and establishes circulation. Furthermore, Homeopathy is advantageous, because the general condition of the patient is preserved during this whole process of gangrene healing. In diabetic cases, one can also appreciate the control of blood sugar levels.
References:
- Samarendra Kumar Mishra(2017). My Experience with Gun Powder in a Septic Gangrene Case; com
- com.Amputee Statistics You Ought to Know; 2014.Available from: http://www.advancedamputees.com/amputee-statistics-you-ought-know. [Last accessed on 2014 May 20]
- Cousin N.Anatomy of an Illness as Perceived by the Patient. 1st New York: Norton; 1979.
- Ertl JP, Brackett WJ, Ertl W, Pritchett JW, Calhoun J, editors. Medscape: Medscape Access; 2014.Emedicine.medscape.com.Availablefrom: http://www.emedicine.medscape.com/article/1232102-overview
- George V. Essence of MateriaMedica.New Delhi: B Jain Publishers Pvt Ltd; 1990.
- Gawronska-Kozak B, Bogacki M, Rim JS, Monroe WT, Manuel JA. Scarless skin repair in immunodeficient mice. Wound Repair Regen 2006;14:265-76.
- Kent JT. Lectures on MateriaMedica. New Delhi: B Jain Publishers Pvt Ltd; 1985.
- Murthy K, Murthy DA.(2017) A Case Report on Diabetic Foot Gangrene, Homoeopathic Links; 30(04): 259-261.
- Kurichi JE, Bates BE, Stineman MG. Amputation. In: Stone JH, Blouin M,editors. International Encyclopedia of Rehabilitation; 2010. Available from: http://www.cirrie.buffalo.edu/encyclopedia/en/article/251/. [Last accessed on 2014 May 23]
- Macchi C, Giannelli F, Cecchi F, Corcos L, Repice F, Cantini CCollateral circulation in occlusion of lower limbs arteries: An anatomical study and statistical research in 35 old subjects. Ital J AnatEmbryol1996;10:89-96.
- Murrant CL. Structural and functional limitations of the collateral circulation in peripheral artery disease. J Physiol 2008;586 (pt24): p.5845.
- Shetty P (2012). Diabetic Foot (Gangrene) is Curable by Homeopathy,homeobook.com
- Mishra SP (2017)No Amputation: Homeopathy Saves the Case, Homeopathic Links; 30(01):048-051.
- Hahnemann S., Boericke W, Krauss J. Organon of Medicine. New Delhi: B Jain Publishers Pvt Ltd; 1992.
- SeemaMahesh, Mahesh Mallappa, George Vithoulkas (2015)Gangrene, IJRH.9(2): 114-122.
- Vithoulkas Compass.N.P; 2014.Available from: http://www.Vithoulkascompass.com.[Last accessed on 2014 Feb 23].
- Vithoulkas G, Woensel E. Levels of health. 1st Alonissos, Greece:International Academy of Classical Homeopathy; 2010.