One possibility to determine the right cell salts is to look for certain signs in the face.
This approach is called “face analysis” or “facial diagnosis”.
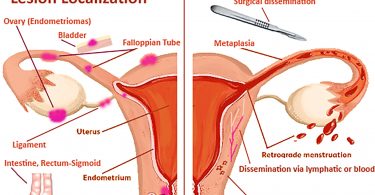
The facial diagnosis is based on the idea, that the absence of certain minerals develops certain signs on the face, as for example the colouring of the face or the state and the vigour of the skin.
Kurt Hickethier, the developer of the face analysis
The face analysis was discovered by Dr. Schüssler and was developed by one of his followers: Kurt Hickethier.
Kurt Hickethier led a sanitarium in Ellrich in the Harz (Germany).
He wrote a book about the face analysis which is the standard work to the face analysis even today.
Hickethier thought the facial diagnosis is the best method to recognize an illness and the needed cell salts.
This contradicted even then the prevailing doctrine and also does not fit to the today’s image of a diagnosis, because “diagnosis” is used in the modern usage to recognise a certain illness and to name.
To avoid conflicts with the usual usage of the word “diagnosis”, nowadays one often speaks of “face analysis”.
Nevertheless, the analysis of the face plays the most important role for the identification of the suitable mineral salts.
In the following list you can find the most important signs in the face to the respective mineral salts.
Product tips
12 basic cell salts
No. 1. (1) Calcium fluoride
Square folds around the eyes
Diversified folds below the eyes
Brown black coloring around the eyes
Burst veins
Scales in the face
Cracked lips, corners of mouth, hands, fingers
Periodontosis
Shining skin
No. 2. (2) Calcium phosphate
Waxy skin
Skin color like cheese
White coating of the tongue
Halitosis
White noses and auricles
Sweaty hair
Rough voice
No. 3. (4) Iron phosphate
Reddened forehead, cheeks
Red, hot ears
Red chin
Red tongue
Blue black shade in the nasal root and under the eyes
Grey black colouring around the nose
Pale gums
No. 4. (5) Potassium chloride
Milky skin
Blue white skin colour
Skin like cheese
Swollen lymphatic knots
White coating of the tongue
Mealy skin dandruff
Stuck together eyes
No. 5. (6) Potassium phosphate
Ash-grey skin, mainly in the chin area
Grey ocular part
Sunken temples
Absent expression
Brown coating of the tongue
Dry tongue
Periodontosis
Gum bleeding
Halitosis
No. 6. (7) Potassium sulphate
Brown-yellow skin
Dark eyelids
Yellowish around the mouth
Freckles
Dandruff on viscous base
Sticking head dandruff
Yellow and slimy coating of the tongue
No. 7. (8) Magnesium phosphate
Red, round spots on the cheeks (always or temporarily)
Red spots in the neck
Otherwise pale skin
Convulsions of the corners of mouth
Twitch of the eyelids
No. 8. (9) Sodium chloride
Humid shine on the upper eyelid, like snail mucus (gelatin shine)
Bright eyelids
Big skin pores
Bloated face
Swollen, spongy cheeks
Head dandruff
White seclusions of the eyes
Clear coating of the tongue
Salivary vesicles on the edge of the tongue
Skin rash in the upper forehead
Itch
Dry skin
No. 9. (10) Sodium phosphate
Greasy, dull shine on the forehead
Greasy nose
Big skin pores
Blackhead
Pimple
Pale mucous membranes
Hanging cheeks
Double chin
Tongue yellowish in the back
No. 10. (11) Sodium sulphate
Green-yellow complexion, especially forehead and temples
Bluish redness in the nose
Bluish redness in front of the ears
Redness in the external corner of the eye
Tongue looks dirty and greenish
No. 11. (12) Silica
Shining skin, as varnished (polished shine)
Waxy yellow or pale skin colour
Deep-recumbent eyes
Slip eyelids
Laughter lines
Crow’s-feet
Convulsions of the eyelids
Small skin pores
Vertical wrinkles in front of the ears
Brittle hair
Dry nose
No. 12. (3) Calcium sulphate
Whiteness, alabaster-like skin colouring (like gypsum)
Only few signs in the face
Liver spots
Brown spots